Global cancer control: responding to the growing burden, rising costs and inequalities in access
- PMID: 29464109
- PMCID: PMC5812392
- DOI: 10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000285
Global cancer control: responding to the growing burden, rising costs and inequalities in access
Abstract
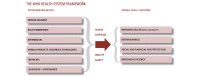
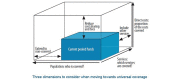
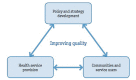
The cancer burden is rising globally, exerting significant strain on populations and health systems at all income levels. In May 2017, world governments made a commitment to further invest in cancer control as a public health priority, passing the World Health Assembly Resolution 70.12 on cancer prevention and control within an integrated approach. In this manuscript, the 2016 European Society for Medical Oncology Leadership Generation Programme participants propose a strategic framework that is in line with the 2017 WHO Cancer Resolution and consistent with the principle of universal health coverage, which ensures access to optimal cancer care for all people because health is a basic human right. The time for action is now to reduce barriers and provide the highest possible quality cancer care to everyone regardless of circumstance, precondition or geographic location. The national actions and the policy recommendations in this paper set forth the vision of its authors for the future of global cancer control at the national level, where the WHO Cancer Resolution must be implemented if we are to reduce the cancer burden, avoid unnecessary suffering and save as many lives as possible.
Keywords: cancer treatment inequalities; global cancer burden; global cancer control.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: AE: Currently conducting research sponsored by AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Celltrion, Novartis, Roche. JT: Advisory Boards for Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Chugai, Genentech, Lilly, MSD, Merck Serono, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Symphogen, Taiho, and Takeda. FCi: Advisory Boards: Merck Serono, Amgen, Roche, Bayer, Lilly, Servier. Research funding: Bayer, Roche, Merck Serono. GP: Honorarium for advisory boards or speakers fee: Roche, Celgene, Shire, Merck, Amgen, Lilly, BMS, Servier, Taiho, Halozyme, Sanofi. PC: Honoraria for consultancy/advisory role and/or for lectures from: Bayer, Blueprint Medicines, Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Nektar Ther., Novartis, Pfizer, PharmaMar. At his institution, his Unit received funds for research from: AmgenDompé, Arog Pharmaceuticals, Bayer, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Daiichi Sankyo Pharma, Epizyme Inc., Novartis, PharmaMar. MS: Conducts research sponsored by Janssen Pharmaceuticals. Advisory Boards: BMS, Novartis, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Leo Pharma. Speaker bureau for BMA, Novartis. Travel funding: Novartis, BMS, Astellas, Ipsen. All other authors declare no competing interests related to this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Global health observatory: the data repository. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2017. (accessed 1 Jun 2017).
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, et al. . GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2013. (accessed 1 Jun 2017).
-
- Open database: IHME. http://www.healthdata.org/data-visualization/financing-global-health
-
- Medicines Use and Spending in the U.S.A Review of 2016 and Outlook to 2021. https://www.iqvia.com/institute/reports/medicines-use-and-spending-in-th....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

