Quiescent Tissue Stem Cells Evade Immune Surveillance
- PMID: 29466757
- PMCID: PMC5824652
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.02.001
Quiescent Tissue Stem Cells Evade Immune Surveillance
Abstract
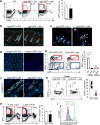
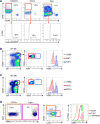
Stem cells are critical for the maintenance of many tissues, but whether their integrity is maintained in the face of immunity is unclear. Here we found that cycling epithelial stem cells, including Lgr5+ intestinal stem cells, as well as ovary and mammary stem cells, were eliminated by activated T cells, but quiescent stem cells in the hair follicle and muscle were resistant to T cell killing. Immune evasion was an intrinsic property of the quiescent stem cells resulting from systemic downregulation of the antigen presentation machinery, including MHC class I and TAP proteins, and is mediated by the transactivator NLRC5. This process was reversed upon stem cell entry into the cell cycle. These studies identify a link between stem cell quiescence, antigen presentation, and immune evasion. As cancer-initiating cells can derive from stem cells, these findings may help explain how the earliest cancer cells evade immune surveillance.
Keywords: MHC class I; Nlrc5; T cell; antigen presentation; hair follicle; immune privilege; immunology; intestine; quiescence; stem cells.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Stem Cells Cycle toward Immune Surveillance.Immunity. 2018 Feb 20;48(2):187-190. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.02.006. Immunity. 2018. PMID: 29466747
-
Stem cells: Escape from the Jedi.Nat Rev Immunol. 2018 Apr;18(4):224. doi: 10.1038/nri.2018.18. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29503454 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barker N. Adult intestinal stem cells: critical drivers of epithelial homeostasis and regeneration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:19–33. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ, et al. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 2007;449:1003–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

