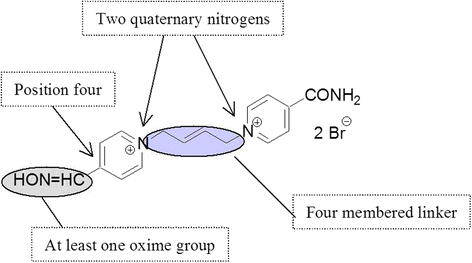
A newly developed oxime K203 is the most effective reactivator of tabun-inhibited acetylcholinesterase
- PMID: 29467029
- PMCID: PMC5822599
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-018-0196-3
A newly developed oxime K203 is the most effective reactivator of tabun-inhibited acetylcholinesterase
Abstract
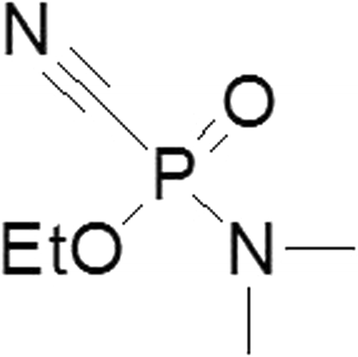
Background: Based on in vitro and in vivo rat experiments, the newly developed acetylcholinesterase (AChE) reactivator, K203, appears to be much more effective in the treatment of tabun poisonings than currently fielded oximes.
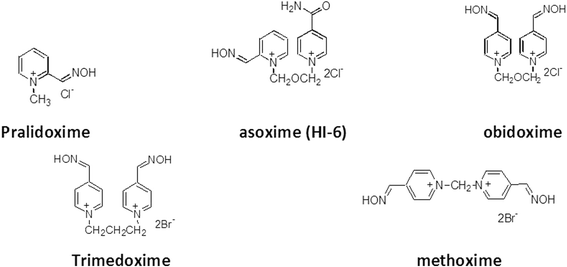
Methods: To determine if this reactivating efficacy would extend to humans, studies were conducted in vitro using human brain homogenate as the source of AChE. The efficacy of K203 was compared with commercially available oximes; pralidoxime, obidoxime and asoxime (HI-6).
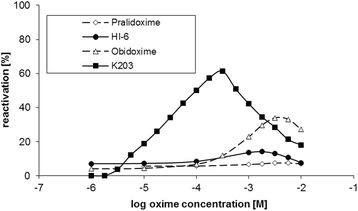
Results: Reactivation studies showed that K203 was the most effective reactivator with a second order kinetic constant (kr) of 2142 min- 1. M- 1, which was 51 times higher than that obtained for obidoxime (kr = 42 min- 1. M- 1). Both pralidoxime and asoxime (HI-6) failed to significantly reactivate tabun-inhibited human AChE.
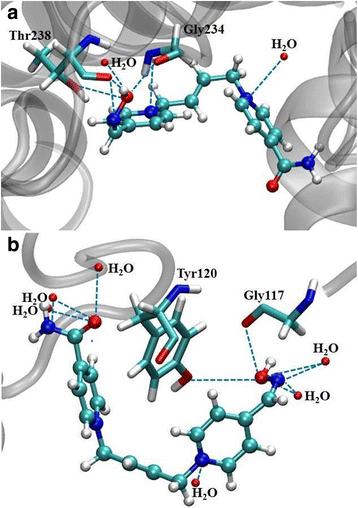
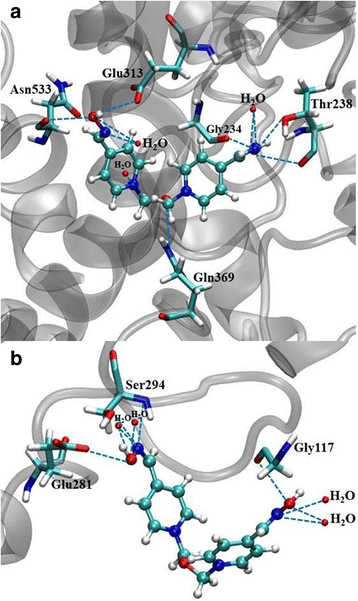
Discussion: According to these results and previous studies, using K203, it appears that oxime K203 is the most effective reactivator of tabun-inhibited cholinesterase in several species including humans and should be considered as a possible medical countermeasure to tabun exposure.
Keywords: Antidotes; Chemical warfare agents; Oxime; Poisoning; Reactivator; Treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Experiments were approved in compliance with relevant laws and institutional guidelines and were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Military Health Sciences in Hradec Kralove (Czech Republic).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An evaluation of therapeutic and reactivating effects of newly developed oximes (K156, K203) and commonly used oximes (obidoxime, trimedoxime, HI-6) in tabun-poisoned rats and mice.Toxicology. 2008 Jan 20;243(3):311-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2007.10.015. Epub 2007 Oct 26. Toxicology. 2008. PMID: 18054821
-
Reactivating potency of obidoxime, pralidoxime, HI 6 and HLö 7 in human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase inhibited by highly toxic organophosphorus compounds.Arch Toxicol. 1998 Mar;72(4):237-43. doi: 10.1007/s002040050495. Arch Toxicol. 1998. PMID: 9587020
-
A comparison of reactivating and therapeutic efficacy of bispyridinium acetylcholinesterase reactivator KR-22934 with the oxime K203 and commonly used oximes (obidoxime, trimedoxime, HI-6) in tabun-poisoned rats and mice.Toxicol Mech Methods. 2011 Mar;21(3):241-5. doi: 10.3109/15376516.2010.538750. Epub 2010 Dec 10. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2011. PMID: 21142778
-
The development of new oximes and the evaluation of their reactivating, therapeutic and neuroprotective efficacy against tabun.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008 Oct;8(11):1134-43. doi: 10.2174/138955708785909871. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18855728 Review.
-
Unequal efficacy of pyridinium oximes in acute organophosphate poisoning.Clin Med Res. 2007 Mar;5(1):71-82. doi: 10.3121/cmr.2007.701. Clin Med Res. 2007. PMID: 17456837 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toxic Injury to Muscle Tissue of Rats Following Acute Oximes Exposure.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 6;9(1):1457. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37837-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30728420 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Interaction Modes and Reactivity of Trimedoxime toward MmAChE Inhibited by Nerve Agents: Theoretical and Experimental Aspects.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 5;21(18):6510. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186510. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899591 Free PMC article.
-
Charged pyridinium oximes with thiocarboxamide moiety are equally or less effective reactivators of organophosphate-inhibited cholinesterases compared to analogous carboxamides.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):760-767. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2041628. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35193448 Free PMC article.
-
FDA-Approved Oximes and Their Significance in Medicinal Chemistry.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 4;15(1):66. doi: 10.3390/ph15010066. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35056123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Spirocyclic Chromane Derivatives as a Potential Treatment of Prostate Cancer.Molecules. 2021 May 25;26(11):3162. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113162. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34070610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calic M, Lucic VA, Radic B, Jelic D, Jun D, Kuca K, Kovarik Z. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of pyridinium oximes: mode of interaction with acetylcholinesterase, effect on tabun- and soman-poisoned mice and their cytotoxicity. Toxicol. 2006;219(1-3):85–96. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2005.11.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

