Ranolazine Attenuates Trastuzumab-Induced Heart Dysfunction by Modulating ROS Production
- PMID: 29467663
- PMCID: PMC5808165
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00038
Ranolazine Attenuates Trastuzumab-Induced Heart Dysfunction by Modulating ROS Production
Abstract
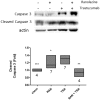
The ErbB2 blocker trastuzumab improves survival in oncologic patients, but can cause cardiotoxicity. The late Na+ current inhibitor ranolazine has been shown to counter experimental HF, including doxorubicin cardiotoxicity (a condition characterized by derangements in redox balance), by lowering the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Since ErbB2 can modulate ROS signaling, we tested whether trastuzumab cardiotoxicity could be blunted by ranolazine via redox-mediated mechanisms. Trastuzumab decreased fractional shortening and ejection fraction in mice, but ranolazine prevented heart dysfunction when co-administered with trastuzumab. Trastuzumab cardiotoxicity was accompanied by elevations in natriuretic peptides and matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) mRNAs, which were not elevated with co-treatment with ranolazine. Trastuzumab also increased cleavage of caspase-3, indicating activation of the proapoptotic machinery. Again, ranolazine prevented this activation. Interestingly, Neonatal Rat Ventricular Myocytes (NRVMs), labeled with MitoTracker Red and treated with trastuzumab, showed only a small increase in ROS compared to baseline conditions. We then stressed trastuzumab-treated cells with the beta-agonist isoproterenol to increase workload, and we observed a significant increase of probe fluorescence, compared with cells treated with isoproterenol alone, reflecting induction of oxidative stress. These effects were blunted by ranolazine, supporting a role for INa inhibition in the regulation of redox balance also in trastuzumab cardiotoxicity.
Keywords: heart failure; heart function; oxidative stress; ranolazine; trastuzumab cardiotoxicity.
Figures



References
-
- Arcaro A., Pirozzi F., Angelini A., Chimenti C., Crotti L., Giordano C., et al. . (2016). Novel perspectives in redox biology and pathophysiology of failing myocytes: modulation of the intramyocardial redox milieu for therapeutic interventions-a review article from the working group of cardiac cell biology, Italian society of cardiology. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016:6353469. 10.1155/2016/6353469 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armenian S. H., Lacchetti C., Barac A., Carver J., Constine L. S., Denduluri N., et al. . (2017). Prevention and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 35, 893–911. 10.1200/JCO.2016.70.5400 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Belmonte F., Das S., Sysa-Shah P., Sivakumaran V., Stanley B., Guo X., et al. . (2015). ErbB2 overexpression upregulates antioxidant enzymes, reduces basal levels of reactive oxygen species, and protects against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 309, H1271–H1280. 10.1152/ajpheart.00517.2014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bers D. M. (2001). Excitation–Contraction Coupling and Cardiac Contractile Force, 2nd Edn. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

