Clinical features, antimicrobial susceptibilities, and treatment outcomes of patients with culture positive endophthalmitis after penetrating keratoplasty
- PMID: 29468222
- PMCID: PMC5787880
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2018.01.011
Clinical features, antimicrobial susceptibilities, and treatment outcomes of patients with culture positive endophthalmitis after penetrating keratoplasty
Abstract
Purpose: To report the clinical features organisms and treatment outcomes in patients with endophthalmitis after penetrating keratoplasty (PK).
Methods: Retrospective noncomparative case series.
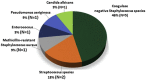
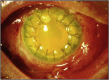
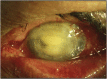
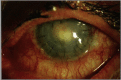
Results: Eleven eyes of 11 patients with culture positive endophthalmitis after PK were included. The time to diagnosis of endophthalmitis from last PK was less than 1 week in 3/11 (27%), between 1 and 4 weeks in 3/11 (27%), and greater than one month in 5/11 (46%) (range 2-924 days). The distribution of isolates included gram positive (GP) 9/11 (82%), gram negative (GN) 1/11 (9%), and fungal 1/11 (9%) species, respectively. Of GP bacteria tested, 9/9 (100%) were sensitive to Vancomycin. Of fungal isolates tested, none (0/1) were sensitive to Amphoteracin, Fluconazole, and/or Voriconazole. Among patients with rim culture data available, 1/7 (14%) donor rims were culture positive for Candida glabrata and 6/7 (86%) were culture negative. Patients were treated with primary tap and inject in 10/11 (91%) and primary vitrectomy in 1/11 (9%). VA of ≥5/200 was present in 2/11 (18%) at time of endophthalmitis diagnosis, and was recorded in 6/11 (55%) at last follow-up.
Conclusions and importance: Patients with endophthalmitis after PK presented at variable time points after surgery. Gram positive organisms were the most common isolate. VA outcomes after treatment were generally poor.
Keywords: BPEI, Bascom Palmer Eye Institute; CE, cataract extraction; DMEK, Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty; DSAEK, descemet stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty; Endophthalmitis; GN, gram negative; GP, Gram positive; HM, Hand motion; IOL, intraocular lens implant; LP, Light perception; NLP, No light perception; PK, penetrating keratoplasty; PPV, vitrectomy; Penetrating keratoplasty; TAP, tap and inject.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Candida Endophthalmitis After Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty With Grafts From Both Eyes of a Donor With Possible Systemic Candidiasis.Cornea. 2018 Apr;37(4):515-518. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000001333. Cornea. 2018. PMID: 29303885 Free PMC article.
-
Acute endophthalmitis after penetrating and endothelial keratoplasty at a tertiary eye care center over a 13-year period.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020 Nov;68(11):2445-2450. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_71_20. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 33120636 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal endophthalmitis after descemet stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty--a case report.Cornea. 2010 Mar;29(3):346-9. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0b013e3181a9d0c0. Cornea. 2010. PMID: 20118788
-
Infectious interface keratitis (IIK) following lamellar keratoplasty: A literature review.Ocul Surf. 2019 Oct;17(4):635-643. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Ocul Surf. 2019. PMID: 31415815
-
Delayed-onset bleb-associated endophthalmitis: clinical features and visual acuity outcomes.Ophthalmology. 2002 May;109(5):985-91. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(02)00965-x. Ophthalmology. 2002. PMID: 11986108 Review.
Cited by
-
[Treatment of postoperative endophthalmitis : Operate or only inject?].Ophthalmologe. 2021 Mar;118(3):219-229. doi: 10.1007/s00347-021-01320-9. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Ophthalmologe. 2021. PMID: 33566160 Review. German.
-
Intensive care unit time and prolonged enucleation to processing interval are associated with donor cornea contamination.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020 Oct;258(10):2241-2249. doi: 10.1007/s00417-020-04758-w. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32613575
References
-
- Leveille A.S., McMullan F.D., Cavanagh H.D. Endophthalmitis following penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmology. 1983;90(1):38–39. - PubMed
-
- Guss R.B., Koenig S., De La Pena W., Marx M., Kaufman H.E. Endophthalmitis after penetrating keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983;95(5):651–658. - PubMed
-
- Pardos G.J., Gallagher M.A. Microbial contamination of donor eyes. A retrospective study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982;100(10):1611–1613. - PubMed
-
- Kloess P.M., Stulting R.D., Waring G.O., Wilson L.A. Bacterial and fungal endophthalmitis after penetrating keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993;115(3):309–316. - PubMed
-
- Taban M., Behrens A., Newcomb R.L., Nobe M.Y., McDonnell P.J. Incidence of acute endophthalmitis following penetrating keratoplasty: a systematic review. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005;123(5):605–609. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

