Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Clinical Practice Guidelines: Joint Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition
- PMID: 29470322
- PMCID: PMC5958910
- DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001889
Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Clinical Practice Guidelines: Joint Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition
Abstract
This document serves as an update of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) 2009 clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in infants and children and is intended to be applied in daily practice and as a basis for clinical trials. Eight clinical questions addressing diagnostic, therapeutic and prognostic topics were formulated. A systematic literature search was performed from October 1, 2008 (if the question was addressed by 2009 guidelines) or from inception to June 1, 2015 using Embase, MEDLINE, the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Clinical Trials. The approach of the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) was applied to define and prioritize outcomes. For therapeutic questions, the quality of evidence was also assessed using GRADE. Grading the quality of evidence for other questions was performed according to the Quality Assessment of Studies of Diagnostic Accuracy (QUADAS) and Quality in Prognostic Studies (QUIPS) tools. During a 3-day consensus meeting, all recommendations were discussed and finalized. In cases where no randomized controlled trials (RCT; therapeutic questions) or diagnostic accuracy studies were available to support the recommendations, expert opinion was used. The group members voted on each recommendation, using the nominal voting technique. With this approach, recommendations regarding evaluation and management of infants and children with GERD to standardize and improve quality of care were formulated. Additionally, 2 algorithms were developed, 1 for infants <12 months of age and the other for older infants and children.
Conflict of interest statement
C.D.L. is a consultant for Allergan, QOL, IBHealth, Nestlé and Merck. Y.V. has participated as a clinical investigator, and/or advisory board member, and/or consultant, and/or speaker for Abbott Nutrition, Aspen, Biogaia, Biocodex, Danone, Hero, Hypocrata, Mead Johnson Nutrition, Merck, Nestle Nutrition Institute, Nutricia, Olygose, Orafti, Phacobel, Rontis, Sari Husada, United Pharmaceuticals, Wyeth and Yakult. M.C. is a consultant for Abbott Nutrition, Biogaia, Nestec, Mead Johnson Nutrition, Merck Wyeth and Yakult. S.G. is a consultant for Recepots and QOL. F.G. is a consultant for Nestlé, Nutricia and Halyard. A.S. has participated as a clinical investigator, and/or advisory board member, and/or consultant, and/or speaker for Aboca, Angelini, Danone, D.M.G. Italy, Menarini, Miltè, Nestlé, Sucampo, Valeas. N.Th. is a consultant for Danone, Nutricia, Shire Movetis and Sucampo. N.Ti. is a consultant for Rock West Medical and Sucampo. The other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Rachel Rosen MD, MPH: RR is an expert in gastroesophageal reflux disease and aerodigestive disorders.
Yvan Vandenplas MD, PhD: YV is an expert in gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Maartje Singendonk MD: MS is an expert in esophageal physiology.
Michael Cabana MD: MC is a pediatrician with expertise in consensus guideline
Carlo Di Lorenzo MD: CD is an expert in pediatric motility disorders and gastroesophageal reflux disease
Frederic Gottrand MD: FG is an expert in esophagitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease
Sandeep Gupta MD: SG is an expert in esophageal diseases.
Miranda Langendam PhD: ML is aguideline methodologist
Annamaria Staiano MD: AS is an expert in pediatric motility disorders and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Nikhil Thapar MD: NT is an expert in pediatric motility disorders.
Neelesh Tipnis MD: NT is an expert in pediatric motility disorders.
Merit Tabbers MD, PhD: MT is an expert in gastroesophageal reflux disease.
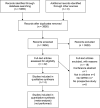
Figures







References
-
- Vandenplas Y, Rudolph CD, Di Lorenzo C, et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009;49(4):498–547. - PubMed
-
- Shekelle P, Woolf S, Grimshaw JM, et al. Developing clinical practice guidelines: reviewing, reporting, and publishing guidelines; updating guidelines; the emerging issues of enhancing guideline implementability and accounting for comorbid conditions in guideline development. Implement Sci. 2012;7:62. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brouwers MC, Kho ME, Browman GP, et al. AGREE II: advancing guideline development, reporting, and evaluation in health care. Prev Med. 2010;51(5):421–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

