Human Factors Risk Analyses of a Doffing Protocol for Ebola-Level Personal Protective Equipment: Mapping Errors to Contamination
- PMID: 29471368
- PMCID: PMC6927873
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cix957
Human Factors Risk Analyses of a Doffing Protocol for Ebola-Level Personal Protective Equipment: Mapping Errors to Contamination
Abstract
Background: Doffing protocols for personal protective equipment (PPE) are critical for keeping healthcare workers (HCWs) safe during care of patients with Ebola virus disease. We assessed the relationship between errors and self-contamination during doffing.
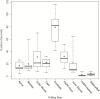
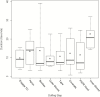
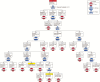
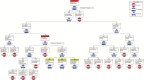
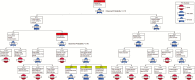
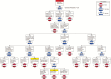
Methods: Eleven HCWs experienced with doffing Ebola-level PPE participated in simulations in which HCWs donned PPE marked with surrogate viruses (ɸ6 and MS2), completed a clinical task, and were assessed for contamination after doffing. Simulations were video recorded, and a failure modes and effects analysis and fault tree analyses were performed to identify errors during doffing, quantify their risk (risk index), and predict contamination data.
Results: Fifty-one types of errors were identified, many having the potential to spread contamination. Hand hygiene and removing the powered air purifying respirator (PAPR) hood had the highest total risk indexes (111 and 70, respectively) and number of types of errors (9 and 13, respectively). ɸ6 was detected on 10% of scrubs and the fault tree predicted a 10.4% contamination rate, likely occurring when the PAPR hood inadvertently contacted scrubs during removal. MS2 was detected on 10% of hands, 20% of scrubs, and 70% of inner gloves and the predicted rates were 7.3%, 19.4%, 73.4%, respectively. Fault trees for MS2 and ɸ6 contamination suggested similar pathways.
Conclusions: Ebola-level PPE can both protect and put HCWs at risk for self-contamination throughout the doffing process, even among experienced HCWs doffing with a trained observer. Human factors methodologies can identify error-prone steps, delineate the relationship between errors and self-contamination, and suggest remediation strategies.
Figures
References
-
- Edmond MB, Diekema DJ, Perencevich EN. Ebola virus disease and the need for new personal protective equipment. JAMA 2014; 312:2495–6. - PubMed
-
- Fischer WA 2nd, Hynes NA, Perl TM. Protecting health care workers from Ebola: personal protective equipment is critical but is not enough. Ann Intern Med 2014; 161:753–4. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC tightened guidance for U.S. healthcare workers on personal protective equipment for Ebola Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2014/fs1020-ebola-personal-protective.... Accessed 18 May 2017.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidance on personal protective equipment (PPE) to be used by healthcare workers during management of patients with confirmed Ebola or persons under investigation (PUIs) for Ebola who are clinically unstable or have bleeding, vomiting, or diarrhea in U.S. hospitals, including procedures for donning and doffing PPE Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/healthcare-us/ppe/guidance.html. Accessed 18 May 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

