Tumor-promoting properties of miR-8084 in breast cancer through enhancing proliferation, suppressing apoptosis and inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- PMID: 29471858
- PMCID: PMC5824560
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-018-1419-5
Tumor-promoting properties of miR-8084 in breast cancer through enhancing proliferation, suppressing apoptosis and inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is one of the most frequent malignancies and the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality in women. MicroRNAs play a key role in breast cancer development and progression. microRNA(miR)-8084 has been observed an aberrant expression in breast cancer. However, the functions and regulatory axes of miR-8084, particularly in breast cancer, were not entirely clear.
Methods: miR-8084 expression in breast cancer were investigated in a GEO dataset by in silico analysis and in 42 paired tumor tissues by qPCR. The effects of deregulation of miR-8084 on breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro and tumorigenicity in vivo were examined by colony-formation assay, wound healing assay, transwell assay and nude mouse subcutaneous tumor formation model. The target gene of miR-8084 were predicted by TargetScan and miRDB, and confirmed by luciferase reporter system. The roles of miR-8084 in the breast cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) were investigated by MTS, FACS and associated-marker detection by western blot.
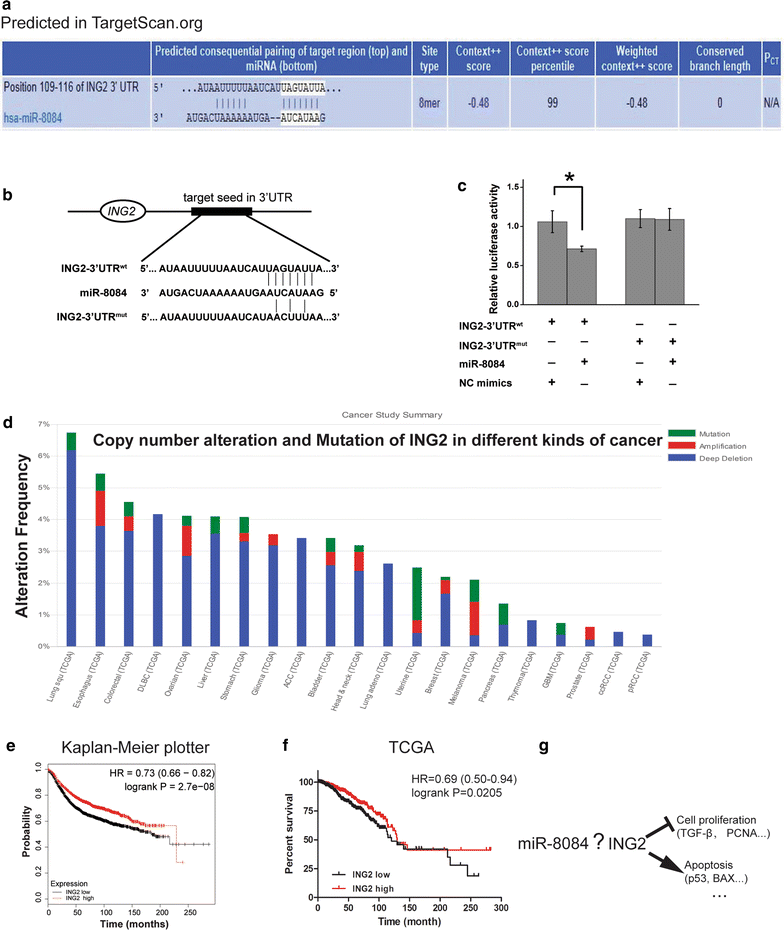
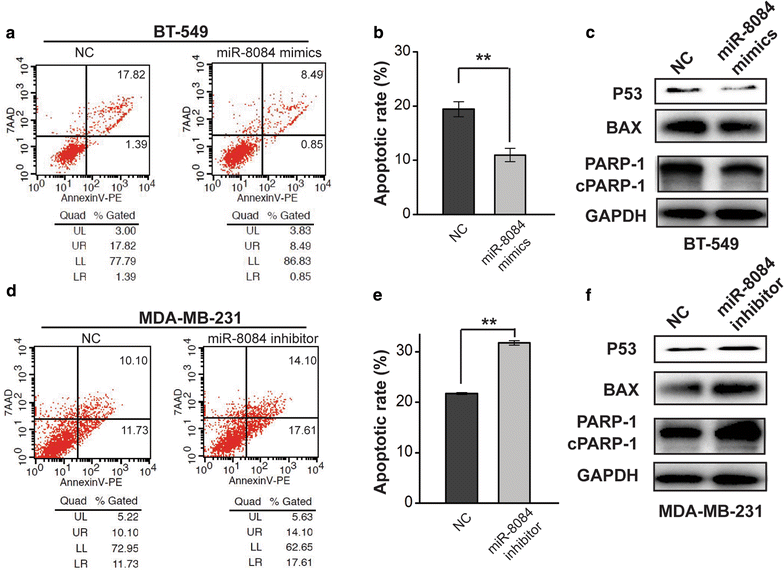
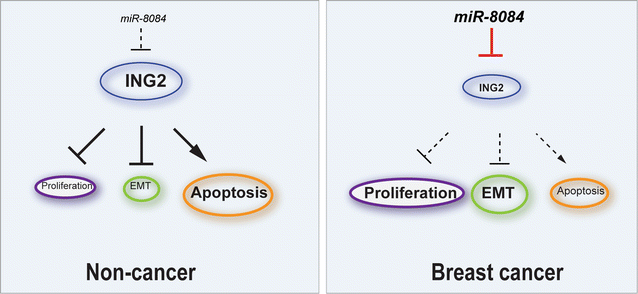
Results: miR-8084 is significantly up-regulated in both serum and malignant tissues from the source of breast cancer patients. miR-8084 promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells by activating ERK1/2 and AKT. Meanwhile miR-8084 inhibits apoptosis by decreasing p53-BAX related pathway. miR-8084 also enhances migration and invasion by inducing EMT. Moreover, the tumor suppressor ING2 is a potential target of miR-8084, and miR-8084 regulatory axes contribute to pro-tumor effect, at least partially through regulating ING2.
Conclusion: Our results strongly suggest that miR-8084 functions as an oncogene that promotes the development and progression of breast cancer, and miR-8084 is a potential new diagnostic marker and therapeutic target of breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; ING2; Tumorigenesis; miR-8084.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Targeting of SPP1 by microRNA-340 inhibits gastric cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(10):18587-18601. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28497. Epub 2019 Apr 5. J Cell Physiol. 2019. Retraction in: J Cell Physiol. 2022 Mar;237(3):2010. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30522. PMID: 30953349 Retracted.
-
Overexpression of microRNA-190 inhibits migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and angiogenesis through suppression of protein kinase B-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway via binding to stanniocalicin 2 in breast cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(10):17824-17838. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28409. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30993707
-
MicroRNA-498 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of prostate cancer cells and decreases radiation sensitivity by targeting PTEN.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019 Nov;35(11):659-671. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12108. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31332950 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the Biotherapeutics Realm via miR-34a: "Potent Clever Little" Agent in Breast Cancer Therapy.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019;20(8):665-673. doi: 10.2174/1389201020666190617162042. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31244419 Review.
-
MiR-1236: Key controller of tumor development and progression: Focus on the biological functions and molecular mechanisms.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Aug;248:154671. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154671. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37418995 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs and Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 30;12(1):96. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010096. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31906022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs in tumor metastasis: molecular and clinical perspectives.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Nov;78(21-22):6823-6850. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03929-0. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34499209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA DINO promotes cisplatin sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma via the p53-Bax axis.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Apr 28;15(4):2198-2212. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-465. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37197522 Free PMC article.
-
Signatures of genetic variation in human microRNAs point to processes of positive selection and population-specific disease risks.Hum Genet. 2022 Oct;141(10):1673-1693. doi: 10.1007/s00439-021-02423-8. Epub 2022 Mar 6. Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 35249174 Free PMC article.
-
TFAP2A downregulation mediates tumor-suppressive effect of miR-8072 in triple-negative breast cancer via inhibiting SNAI1 transcription.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 18;26(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01858-x. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38890750 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

