HDL in CKD-The Devil Is in the Detail
- PMID: 29472417
- PMCID: PMC5967756
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2017070798
HDL in CKD-The Devil Is in the Detail
Abstract
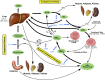
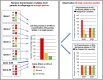
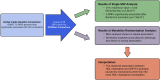
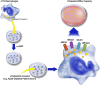
The picture of HDL cholesterol (HDL-C) as the "good" cholesterol has eroded. This is even more surprising because there exists strong evidence that HDL-C is associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD) in the general population as well as in patients with impairment of kidney function and/or progression of CKD. However, drugs that dramatically increase HDL-C have mostly failed to decrease CVD events. Furthermore, genetic studies took the same line, as genetic variants that have a pronounced influence on HDL-C concentrations did not show an association with cardiovascular risk. For many, this was not surprising, given that an HDL particle is highly complex and carries >80 proteins and several hundred lipid species. Simply measuring cholesterol might not reflect the variety of biologic effects of heterogeneous HDL particles. Therefore, functional studies and the involvement of HDL components in the reverse cholesterol transport, including the cholesterol efflux capacity, have become a further focus of study during recent years. As also observed for other aspects, CKD populations behave differently compared with non-CKD populations. Although clear disturbances have been observed for the "functionality" of HDL particles in patients with CKD, this did not necessarily translate into clear-cut associations with outcomes.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; cholesterol transport; high-density lipoprotein; lipids; progression of chronic renal failure; reverse.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Vaziri ND, Navab M, Fogelman AM: HDL metabolism and activity in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 6: 287–296, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Speer T, Rohrer L, Blyszczuk P, Shroff R, Kuschnerus K, Kränkel N, et al. : Abnormal high-density lipoprotein induces endothelial dysfunction via activation of Toll-like receptor-2. Immunity 38: 754–768, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Morena M, Cristol JP, Dantoine T, Carbonneau MA, Descomps B, Canaud B: Protective effects of high-density lipoprotein against oxidative stress are impaired in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15: 389–395, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Annema W, von Eckardstein A: Dysfunctional high-density lipoproteins in coronary heart disease: Implications for diagnostics and therapy. Transl Res 173: 30–57, 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

