ADAM17 is required for EGF-R-induced intestinal tumors via IL-6 trans-signaling
- PMID: 29472497
- PMCID: PMC5881468
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20171696
ADAM17 is required for EGF-R-induced intestinal tumors via IL-6 trans-signaling
Abstract
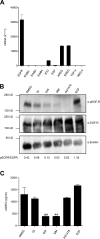
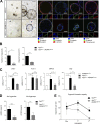
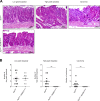
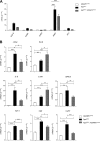
Colorectal cancer is treated with antibodies blocking epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R), but therapeutic success is limited. EGF-R is stimulated by soluble ligands, which are derived from transmembrane precursors by ADAM17-mediated proteolytic cleavage. In mouse intestinal cancer models in the absence of ADAM17, tumorigenesis was almost completely inhibited, and the few remaining tumors were of low-grade dysplasia. RNA sequencing analysis demonstrated down-regulation of STAT3 and Wnt pathway components. Because EGF-R on myeloid cells, but not on intestinal epithelial cells, is required for intestinal cancer and because IL-6 is induced via EGF-R stimulation, we analyzed the role of IL-6 signaling. Tumor formation was equally impaired in IL-6-/- mice and sgp130Fc transgenic mice, in which only trans-signaling via soluble IL-6R is abrogated. ADAM17 is needed for EGF-R-mediated induction of IL-6 synthesis, which via IL-6 trans-signaling induces β-catenin-dependent tumorigenesis. Our data reveal the possibility of a novel strategy for treatment of colorectal cancer that could circumvent intrinsic and acquired resistance to EGF-R blockade.
© 2018 Crown copyright. The government of Australia, Canada, or the UK ("the Crown") owns the copyright interests of authors who are government employees. The Crown Copyright is not transferable.
Figures





References
-
- Atreya R., Mudter J., Finotto S., Müllberg J., Jostock T., Wirtz S., Schütz M., Bartsch B., Holtmann M., Becker C., et al. 2000. Blockade of interleukin 6 trans signaling suppresses T-cell resistance against apoptosis in chronic intestinal inflammation: Evidence in Crohn disease and experimental colitis in vivo. Nat. Med. 6:583–588. 10.1038/75068 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

