HU protein is involved in intracellular growth and full virulence of Francisella tularensis
- PMID: 29473442
- PMCID: PMC5955460
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1441588
HU protein is involved in intracellular growth and full virulence of Francisella tularensis
Abstract
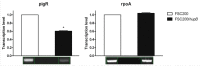
The nucleoid-associated HU proteins are small abundant DNA-binding proteins in bacterial cell which play an important role in the initiation of DNA replication, cell division, SOS response, control of gene expression and recombination. HU proteins bind to double stranded DNA non-specifically, but they exhibit high affinity to abnormal DNA structures as four-way junctions, gaps or nicks, which are generated during DNA damage. In many pathogens HU proteins regulate expression of genes involved in metabolism and virulence. Here, we show that the Francisella tularensis subsp. holarctica gene locus FTS_0886 codes for functional HU protein which is essential for full Francisella virulence and its resistance to oxidative stress. Further, our results demonstrate that the recombinant FtHU protein binds to double stranded DNA and protects it against free hydroxyl radicals generated via Fenton's reaction. Eventually, using an iTRAQ approach we identified proteins levels of which are affected by the deletion of hupB, among them for example Francisella pathogenicity island (FPI) proteins. The pleiotropic role of HU protein classifies it as a potential target for the development of therapeutics against tularemia.
Keywords: DNA binding protein; FPI; Francisella; HU protein; nucleoid-associated protein; virulence.
Figures


References
-
- McDonald MK, Cowley SC, Nano FE. Temperature-sensitive lesions in the Francisella novicida valA gene cloned into an Escherichia coli msbA lpxK mutant affecting deoxycholate resistance and lipopolysaccharide assembly at the restrictive temperature. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:7638–7643. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.24.7638-7643.1997 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
