Correction of radiographic measurements of acetabular cup wear for variations in pelvis orientation
- PMID: 29473454
- PMCID: PMC5846875
- DOI: 10.1177/0954411918754924
Correction of radiographic measurements of acetabular cup wear for variations in pelvis orientation
Abstract
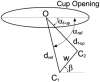
Radiographic measurement of two-dimensional acetabular cup wear is usually carried out on a series of follow-up radiographs of the patient's pelvis. Since the orientation of the pelvis might not be consistent at every X-ray examination, the resulting change in view of the wear plane introduces error into the linear wear measurement. This effect is amplified on some designs of cup in which the centre of the socket is several millimetres below the centre of the cup or circular wire marker. This study describes the formulation of a mathematical method to correct radiographic wear measurements for changes in pelvis orientation. A mathematical simulation of changes in cup orientation and wear vectors caused by pelvic tilt was used to confirm that the formulae corrected the wear exactly if the radiographic plane of the reference radiograph was parallel to the true plane of wear. An error analysis showed that even when the true wear plane was not parallel to the reference radiographic plane, the formulae could still provide a useful correction. A published correction formula was found to be ineffective.
Keywords: Hip prosthesis; acetabular cup wear; pelvic orientation; pelvic tilt; radiographic measurement; total hip replacement; wear correction; wear measurement.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Green TR, Fisher J, Mathews JB, et al. Effect of size and dose on bone resorption of macrophages by in vitro clinically relevant ultra high molecular weight polyethylene particles. J Biomed Mater Res 2000; 53: 490–497. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi A, Freeman MAR, Bonfield W, et al. Number of polyethylene particles and osteolysis in total joint replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1997; 79-B: 844–848. - PubMed
-
- Orishimo KF, Claus AM, Sychterz CJ, et al. Relationship between polyethylene wear and osteolysis in hips with a second-generation porous-coated cementless cup after seven years of follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003; 85: 1095–1099. - PubMed
-
- Dumbleton JH, Manley MT, Edidin AA. A literature review of the association between wear rate and osteolysis in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2002; 17: 649–661. - PubMed
-
- Rajpura A, Kendoff D, Board TN. The current state of bearing surfaces in total hip replacement. Bone Joint J 2014; 96-B: 147–156. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

