High Virologic Failure Rates with Maraviroc-Based Salvage Regimens Among Indian Patients: A Preliminary Analysis-Maraviroc Effectiveness in HIV-1 Subtype C
- PMID: 29473485
- PMCID: PMC6748454
- DOI: 10.1177/2325958218759211
High Virologic Failure Rates with Maraviroc-Based Salvage Regimens Among Indian Patients: A Preliminary Analysis-Maraviroc Effectiveness in HIV-1 Subtype C
Abstract
Background: There is no information on the clinical effectiveness of Maraviroc (MVC) amongst People Living with HIV (PLHIV) in India infected with HIV-1 Subtype C viruses.
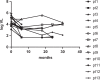
Methods: We conducted a retrospective chart review of adult PLHIV on MVC based Antiretroviral (ARV) regimens for at least 6 months. Maraviroc was initiated amongst PLHIV with documented R5 tropic viruses (determined by in-house population sequencing of the V3 loop in triplicate and interpreted using the Geno2Pheno algorithm) in combination with an Optimized Background regimen (designed using genotypic resistance testing and past ARV history). Plasma viral loads (PVL) are performed 6 months post-initiation and annually thereafter. Primary outcome d. Median duration on MVC treatment was 1.8 years (range 1-2.9 years) while median duration of ART prior to switching to MVC was 13 years. Maraviroc was combined with Darunavir/ritonavir (DRV/r) (n=10), Atazanavir/r (ATV/r) (n=2) and Lopinavir/r (LPV/r) (n=1). All PLHIV were infected with HIV-1 Subtype C. Only 23.3% PLHIV achieved virologic suppression at 6 months and sustained it for 2.3 years. Median CD4 count change from baseline was +117 (n=13), +228 (n=10), +253 (n=9), and +331 (n=4) at 6, 12, 18 and 24 months respectively. Repeat tropism among patients with virologic failure demonstrated R5 virus.
Conclusions: High rates of virologic failure was seen when MVC was used amongst treatment experienced PLHIV infected with HIV-1 Subtype C in India. was the proportion of PLHIV with virologic success (PVL<50 copies/ml) at last follow up visit.
Results: Data on 13 PLHIV were analyze.
Keywords: India; maraviroc; subtype C; virologic failure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Virologic response, early HIV-1 decay, and maraviroc pharmacokinetics with the nucleos(t)ide-free regimen of maraviroc plus darunavir/ritonavir in a pilot study.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2013 Oct 1;64(2):167-73. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3182a03d95. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2013. PMID: 23797691 Free PMC article.
-
Maraviroc once-daily nucleoside analog-sparing regimen in treatment-naive patients: randomized, open-label pilot study.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2013 Feb 1;62(2):164-70. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31827b51b5. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2013. PMID: 23187936 Clinical Trial.
-
Characterization of virologic failure patients on darunavir/ritonavir in treatment-experienced patients.AIDS. 2009 Sep 10;23(14):1829-40. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32832cbcec. AIDS. 2009. PMID: 19474650 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the predictive performance of adherence measures for virologic failure detection in people living with HIV: a systematic review and pairwise meta-analysis.AIDS Care. 2019 Jun;31(6):647-659. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2018.1554241. Epub 2018 Dec 5. AIDS Care. 2019. PMID: 30516060
-
Current ART, determinants for virologic failure and implications for HIV drug resistance: an umbrella review.AIDS Res Ther. 2023 Oct 27;20(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12981-023-00572-6. AIDS Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37884997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Teeraananchai S, Chaivooth S, Kerr SJ, et al. Life expectancy after initiation of combination antiretroviral therapy in Thailand. Antivir Ther. 2017;22(5):393–402. - PubMed
-
- Teeraananchai S, Kerr SJ, Amin J, Ruxrungtham K, Law MG. Life expectancy of HIV-positive people after starting combination antiretroviral therapy: a meta-analysis. HIV Med. 2017;18(4):256–266. - PubMed
-
- van Lelyveld SF, Wensing AM, Hoepelman AI. The MOTIVATE trials: maraviroc therapy in antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected patients. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012;10(11):1241–1247. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous