Leader-Follower Formation Control of UUVs with Model Uncertainties, Current Disturbances, and Unstable Communication
- PMID: 29473919
- PMCID: PMC5855002
- DOI: 10.3390/s18020662
Leader-Follower Formation Control of UUVs with Model Uncertainties, Current Disturbances, and Unstable Communication
Abstract
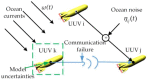
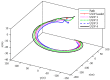
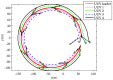
Unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) have rapidly developed as mobile sensor networks recently in the investigation, survey, and exploration of the underwater environment. The goal of this paper is to develop a practical and efficient formation control method to improve work efficiency of multi-UUV sensor networks. Distributed leader-follower formation controllers are designed based on a state feedback and consensus algorithm. Considering that each vehicle is subject to model uncertainties and current disturbances, a second-order integral UUV model with a nonlinear function is established using the state feedback linearized method under current disturbances. For unstable communication among UUVs, communication failure and acoustic link noise interference are considered. Two-layer random switching communication topologies are proposed to solve the problem of communication failure. For acoustic link noise interference, accurate representation of valid communication information and noise stripping when designing controllers is necessary. Effective communication topology weights are designed to represent the validity of communication information interfered by noise. Utilizing state feedback and noise stripping, sufficient conditions for design formation controllers are proposed to ensure UUV formation achieves consensus under model uncertainties, current disturbances, and unstable communication. The stability of formation controllers is proven by the Lyapunov-Razumikhin theorem, and the validity is verified by simulation results.
Keywords: current disturbances; leader-follower formation control; model uncertainties; multi-UUV sensor networks; unstable communication.
Conflict of interest statement
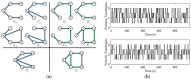
Control gains for the position and velocity communication topologies
Figures


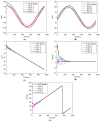
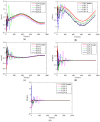
References
-
- Hollinger G.A., Choudhary S., Qarabaqi P., Murphy C., Mitra U., Sukhatme G.S., Stojanovic M., Singh H., Hover F. Underwater data collection using robotic sensor networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2012;30:899–911. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2012.120606. - DOI
-
- Al-Khatib H., Antonelli G., Caffaz A., Caiti A., Casalino G., de Jong I.B., Duarte H., Indiveri G., Jesus S., Kebkal K. The widely scalable Mobile Underwater Sonar Technology (WiMUST) project: An overview; Proceedings of the Oceans 2015; Genova, Italy. 18–21 May 2015; pp. 1–5.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

