Palladium-Catalyzed C-O Cross-Coupling of Primary Alcohols
- PMID: 29474078
- PMCID: PMC5856650
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00325
Palladium-Catalyzed C-O Cross-Coupling of Primary Alcohols
Abstract
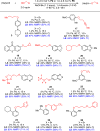
Two catalyst systems are described, which together provide mild and general conditions for the Pd-catalyzed C-O cross-coupling of primary alcohols. For activated substrates, such as electron-deficient aryl halides, the commercially available ligand L2 promotes efficient coupling for a variety of alcohol nucleophiles. In the case of unactivated electrophiles, such as electron-rich aryl halides, the new ligand L8 was developed to improve these challenging C-O bond-forming reactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): MIT has or has filed patents on ligands/precatalysts that are described in the paper from which S.L.B. and former co-workers receive royalty payments.
Figures



References
-
- Fuwa H. Toxins and Biologically Active Compounds from Microalgae. Vol. 1. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 2014. Total Synthesis of Marine Polycyclic Ether Natural Products; pp. 348–412.
- Pitsinos EN, Vidali VP, Couladouros EA. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011;2011:1207.
- Nicolaou KC, Boddy CNC, Bräse S, Winssinger N. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999;38:2096. - PubMed
-
- [accessed Nov 9, 2017];Top Drugs. http://www.pacific.edu/Academics/Schools-and-Colleges/Thomas-J-Long-Scho....
- Roughley SD, Jordan AM. J. Med. Chem. 2011;54:3451. - PubMed
-
- Stevenson TM, Reddy RP. WO2017011288A1. 2017
- Wang X, Liu A, Cao L, Lei M, Ren Y, Zhou B, Huang L, Gao D, Chen H, Cheng L. CN105985246A. 2016
-
- Wang Z. Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ: 2010. Williamson Ether Synthesis; pp. 3026–3030.
-
- Swamy KCK, Kumar NNB, Balaraman E, Kumar KVPP. Chem. Rev. 2009;109:2551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

