Levels of regulatory B cells do not predict serological responses to hepatitis B vaccine
- PMID: 29474139
- PMCID: PMC6037437
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1441653
Levels of regulatory B cells do not predict serological responses to hepatitis B vaccine
Abstract
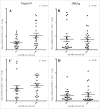
This study investigated the immunomodulatory influence of IL10 producing B regulatory cells, Bregs (CD19+CD24hiCD38hi) to standard Twinrix® vaccination. We also investigated HBsAg specific T-cell mediated IFN-γ responses to Twinrix® which in theory could provide effective immunity despite low anti-HBs titer. A total of 309 hepatitis B negative health care students and workers completed a standard Twinrix® vaccination schedule (0, 1 and 6 months). Depending on the vaccination response the participants were divided in to non-, low- and high responders according to anti-HBs titer (<10, <100 and >1000 mIU/mL respectively) two months after completed vaccination schedule. Blood samples from baseline and after vaccination from all non- and low-responders (23 participants) and the same number of high-responders were used for flow cytometric analyses of IL10 producing Bregs and T-cell mediated IFN-γ responses. A decrease in levels of IL10 producing Bregs was observed after vaccination in high responders compared to non- and low-responders. Compiling non-and low-responders against high-responders showed a lower T-cell mediated IFN-γ response at baseline in non-and low-responders when stimulated with Engerix® vaccine. In contrary no positive correlation between IL10 producing Bregs or IFN-γ positive T-cells and anti-HBs titer was observed. Hence this study cannot prove that levels of IL10 producing Bregs or IFN-γ positive T cell affect HBV vaccine response.
Keywords: Hepatitis B; Interferon γ; Interleukin 10; Twinrix; clinical; flow cytometry; hepatitis; non-responders; vaccinology.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Hepatitis B. Fact sheet N°204. 2015. [accessed 2015September09]; http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs204/en/.
-
- de la Hoz F, Perez L, de Neira M, Hall AJ. Eight years of hepatitis B vaccination in Colombia with a recombinant vaccine: factors influencing hepatitis B virus infection and effectiveness. Int J Infect Dis. 2008;12(2):183–9. Epub 2007/October/05. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2007.06.010. PMID:17913535 - DOI - PubMed
-
- McMahon BJ, Bulkow LR, Singleton RJ, Williams J, Snowball M, Homan C, Parkinson AJ. Elimination of hepatocellular carcinoma and acute hepatitis B in children 25 years after a hepatitis B newborn and catch-up immunization program. Hepatology. 2011;54(3):801–7. Epub 2011/May/28. doi:10.1002/hep.24442. PMID:21618565 - DOI - PubMed
-
- WHO Immunization, Vaccines and Biologicals 2013. [accessed 2015September09]; http://www.who.int/immunization/topics/hepatitis_b/en/.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
