Epitopes for neutralizing antibodies induced by HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein BG505 SOSIP trimers in rabbits and macaques
- PMID: 29474444
- PMCID: PMC5841823
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006913
Epitopes for neutralizing antibodies induced by HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein BG505 SOSIP trimers in rabbits and macaques
Abstract
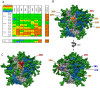
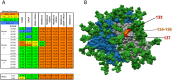
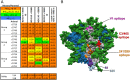
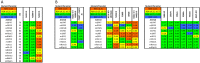
The native-like, soluble SOSIP.664 trimer based on the BG505 clade A env gene of HIV-1 is immunogenic in various animal species, of which the most studied are rabbits and rhesus macaques. The trimer induces autologous neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) consistently but at a wide range of titers and with incompletely determined specificities. A precise delineation of immunogenic neutralization epitopes on native-like trimers could help strategies to extend the NAb response to heterologous HIV-1 strains. One autologous NAb epitope on the BG505 Env trimer is known to involve residues lining a hole in the glycan shield that is blocked by adding a glycan at either residue 241 or 289. This glycan-hole epitope accounts for the NAb response of most trimer-immunized rabbits but not for that of a substantial subset. Here, we have used a large panel of mutant BG505 Env-pseudotyped viruses to define additional sites. A frequently immunogenic epitope in rabbits is blocked by adding a glycan at residue 465 near the junction of the gp120 V5 loop and β24 strand and is influenced by amino-acid changes in the structurally nearby C3 region. We name this new site the "C3/465 epitope". Of note is that the C3 region was under selection pressure in the infected infant from whom the BG505 virus was isolated. A third NAb epitope is located in the V1 region of gp120, although it is rarely immunogenic. In macaques, NAb responses induced by BG505 SOSIP trimers are more often directed at the C3/465 epitope than the 241/289-glycan hole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Escolano A, Dosenovic P, Nussenzweig MC. Progress toward active or passive HIV-1 vaccination. J Exp Med. 2017;214(1):3–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.20161765 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sanders RW, Moore JP. Native-like Env trimers as a platform for HIV-1 vaccine design. Immunol Rev. 2017;275(1):161–82. doi: 10.1111/imr.12481 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ward AB, Wilson IA. The HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein structure: nailing down a moving target. Immunol Rev. 2017;275(1):21–32. doi: 10.1111/imr.12507 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kwong PD. What Are the Most Powerful Immunogen Design Vaccine Strategies? A Structural Biologist’s Perspective. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017;9(11). doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029470 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

