Contrast - in cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 29474744
- PMCID: PMC6071321
- DOI: 10.1111/echo.13845
Contrast - in cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
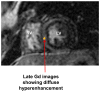
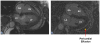
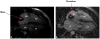
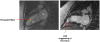
The utility and role of cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) as a non-invasive diagnostic imaging modality has been well recognized in the field of cardiovascular disease. Use of late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) has further enhanced CMR's ability to determine structural, functional, and prognostic information in various cardiovascular diseases. The delivery and distribution of gadolinium as an extracellular agent allows the detection of edema, fibrosis, and infiltration in the myocardium. The pattern of LGE in cardiomyopathies enables us to distinguish among various disease processes non-invasively. Additionally, in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and sudden cardiac death, it helps in decision making in regards to use of implantable cardioverter defibrillator. In the evaluation of cardiac masses, LGE-CMR can often times differentiate between neoplastic and non-neoplastic conditions. In this review, we will discuss the various aspects of gadolinium-based contrast agents, and its application in CMR.
Keywords: cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; contrast imaging.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
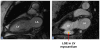
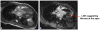
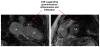
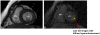
Figures


References
-
- Karamitsos TD, Francis JM, Myerson S, et al. The role of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:1407–1424. - PubMed
-
- Kwon DH, Smedira NG, Rodriguez ER, et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance detection of myocardial scarring in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: correlation with histopathology and prevalence of ventricular tachycardia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:242–249. - PubMed
-
- Soriano CJ, Ridocci F, Estornell J, et al. Noninvasive diagnosis of coronary artery disease in patients with heart failure and systolic dysfunction of uncertain etiology, using late gadolinium-enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:743–748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

