Lanthionine ketimine-5-ethyl ester provides neuroprotection in a zebrafish model of okadaic acid-induced Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 29475037
- PMCID: PMC5865644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2018.02.002
Lanthionine ketimine-5-ethyl ester provides neuroprotection in a zebrafish model of okadaic acid-induced Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
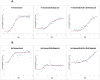
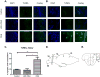
Okadaic acid (OKA) is a protein phosphatase 2A inhibitor that is used to induce neurodegeneration and study disease states such as Alzheimer's disease (AD). Lanthionine ketimine-5-ethyl ester (LKE) is a bioavailable derivative of the naturally occurring brain sulfur metabolite, lanthionine ketimine (LK). In previously conducted studies, LKE exhibited neuroprotective and neurotrophic properties in murine models but its mechanism of action remains to be clarified. In this study, a recently established zebrafish OKA-induced AD model was utilized to further elucidate the neuroprotective and neurotrophic properties of LKE in the context of an AD-like condition. The fish were divided into 3 groups containing 8 fish per group. Group #1 = negative control, Group #2 = 100 nM OKA, Group #3 = 100 nM OKA +500 μM LKE. OKA caused severe cognitive impairments in the zebrafish, but concomitant treatment with LKE protected against cognitive impairments. Further, LKE significantly and substantially reduced the number of apoptotic brain cells, increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and increased phospho-activation of the pro-survival factors pAkt (Ser 473) and pCREB (Ser133). These findings clarify the neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects of LKE by highlighting particular survival pathways that are bolstered by the experimental therapeutic LKE.
Keywords: BDNF; CREB; Lanthionine ketimine-5-ethyl-ester; Okadaic acid; PKB/Akt; Zebrafish.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict(s) of interest: Dr. Hensley is inventor on a patent concerning composition and use of LKE for medical purposes, and holds equity in XoNovo Ltd., a company engaged in development of the compound.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects of Lanthionine Ketimine Ester.Neurosci Lett. 2018 Jan 18;664:28-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.11.018. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 29128626
-
A derivative of the CRMP2 binding compound lanthionine ketimine provides neuroprotection in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia.Neurochem Int. 2012 Dec;61(8):1357-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.09.013. Epub 2012 Oct 2. Neurochem Int. 2012. PMID: 23036362 Free PMC article.
-
Lanthionine ketimine ester provides benefit in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis.J Neurochem. 2015 Jul;134(2):302-14. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13114. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25846048
-
Utilizing zebrafish and okadaic acid to study Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Sep;13(9):1538-1541. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.237111. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 30127109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative functions of the brain transsulfuration pathway represent an underappreciated aspect of brain redox biochemistry with significant potential for therapeutic engagement.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Jan;78:123-34. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.10.581. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25463282 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted imaging of lysosomal zinc ions with a tetrahedral DNA framework fluorescent reporter.Natl Sci Rev. 2024 Sep 12;11(11):nwae307. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwae307. eCollection 2024 Nov. Natl Sci Rev. 2024. PMID: 39440260 Free PMC article.
-
The GSK3β inhibitor, TDZD-8, rescues cognition in a zebrafish model of okadaic acid-induced Alzheimer's disease.Neurochem Int. 2019 Jan;122:31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2018.10.022. Epub 2018 Oct 28. Neurochem Int. 2019. PMID: 30392874 Free PMC article.
-
Human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells treated with okadaic acid express phosphorylated high molecular weight tau-immunoreactive protein species.J Neurosci Methods. 2019 May 1;319:60-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.09.030. Epub 2018 Sep 29. J Neurosci Methods. 2019. PMID: 30278184 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Lanthionine Ketimine Derivatives for Maturation and Proliferative Effects in Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells.ASN Neuro. 2025;17(1):2535963. doi: 10.1080/17590914.2025.2535963. Epub 2025 Jul 21. ASN Neuro. 2025. PMID: 40692140 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Conditional Knockout of Collapsin Response Mediator Protein 2 Ameliorates Disease Severity in a Mouse Model of Multiple Sclerosis.ASN Neuro. 2019 Jan-Dec;11:1759091419892090. doi: 10.1177/1759091419892090. ASN Neuro. 2019. PMID: 31795726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De-Paula VJ, et al. Alzheimer’s disease. Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329–52. - PubMed
-
- Nada SE, Williams FE, Shah ZA. Development of a Novel and Robust Pharmacological Model of Okadaic Acid-induced Alzheimer’s Disease in Zebrafish. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2016;15(1):86–94. - PubMed
-
- Cooper AJ. The role of glutamine transaminase K (GTK) in sulfur and alpha-keto acid metabolism in the brain, and in the possible bioactivation of neurotoxicants. Neurochem Int. 2004;44(8):557–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

