Can P-glycoprotein and β-tubulin polymorphisms be used as genetic markers of resistance in Dirofilaria immitis from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil?
- PMID: 29475454
- PMCID: PMC5824453
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-018-3259-z
Can P-glycoprotein and β-tubulin polymorphisms be used as genetic markers of resistance in Dirofilaria immitis from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil?
Abstract
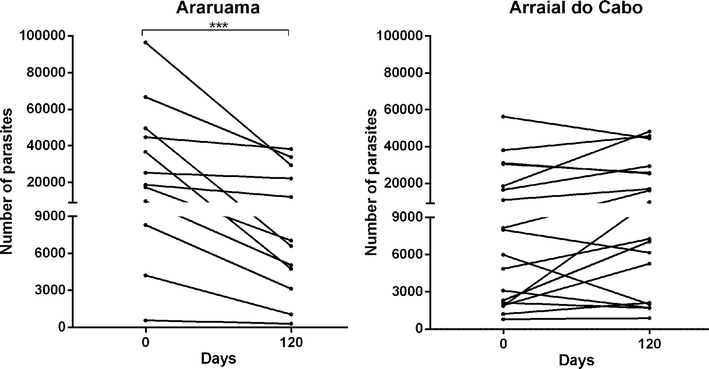
Objective: Dirofilaria immitis, the causative agent of canine heartworm infection, is worldwide the most important filarid to affect domestic dogs. Prevention of this infection is done by macrocyclic lactones, but some reports on the lack of efficacy have been published. Although the actual cause of resistance is unknown, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on a P-glycoprotein ABC transporter and β-tubulin genes have been pointed out as candidates for genetic markers of resistance. We conducted a survey to verify the presence of these suggested genetic markers in microfilariae from 30 naturally infected dogs under macrocyclic lactones treatment living in an endemic area in the state of Rio de Janeiro.
Results: The analysis of these specific SNPs demonstrated no sign of polymorphism on the P-glycoprotein loci, while 72 and 48% of the samples were polymorphic to the first and second SNPs on β-tubulin loci, respectively. This work demonstrates that the P-glycoprotein position 11 and 618 were not polymorphic and, therefore, not suitable as a genetic marker of resistance in Rio de Janeiro whereas both β-tubulin loci were polimorphic. This work points out the difficulty of finding a universal genetic marker for resistance.
Keywords: Dirofilaria immitis; Genetic marker of resistance; Macrocyclic lactones.
Figures
References
-
- Tsiatis AC, Norris-Kirby A, Rich RG, Hafez MJ, Gocke CD, Eshleman JR, Murphy KM. Comparison of Sanger sequencing, pyrosequencing, and melting curve analysis for the detection of KRAS mutations: diagnostic and clinical implications. J Mol Diagn. 2010;12(4):425–432. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2010.090188. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

