Mechanisms of platelet clearance and translation to improve platelet storage
- PMID: 29475962
- PMCID: PMC5887765
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-08-743229
Mechanisms of platelet clearance and translation to improve platelet storage
Abstract
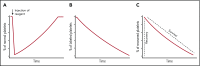
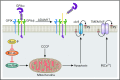
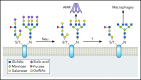
Hundreds of billions of platelets are cleared daily from circulation via efficient and highly regulated mechanisms. These mechanisms may be stimulated by exogenous reagents or environmental changes to accelerate platelet clearance, leading to thrombocytopenia. The interplay between antiapoptotic Bcl-xL and proapoptotic molecules Bax and Bak sets an internal clock for the platelet lifespan, and BH3-only proteins, mitochondrial permeabilization, and phosphatidylserine (PS) exposure may also contribute to apoptosis-induced platelet clearance. Binding of plasma von Willebrand factor or antibodies to the ligand-binding domain of glycoprotein Ibα (GPIbα) on platelets can activate GPIb-IX in a shear-dependent manner by inducing unfolding of the mechanosensory domain therein, and trigger downstream signaling in the platelet including desialylation and PS exposure. Deglycosylated platelets are recognized by the Ashwell-Morell receptor and potentially other scavenger receptors, and are rapidly cleared by hepatocytes and/or macrophages. Inhibitors of platelet clearance pathways, including inhibitors of GPIbα shedding, neuraminidases, and platelet signaling, are efficacious at preserving the viability of platelets during storage and improving their recovery and survival in vivo. Overall, common mechanisms of platelet clearance have begun to emerge, suggesting potential strategies to extend the shelf-life of platelets stored at room temperature or to enable refrigerated storage.
© 2018 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Nieswandt B, Bergmeier W, Rackebrandt K, Gessner JE, Zirngibl H. Identification of critical antigen-specific mechanisms in the development of immune thrombocytopenic purpura in mice. Blood. 2000;96(7):2520-2527. - PubMed
-
- Odell TT Jr, McDonald TP. Life span of mouse blood platelets. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961;106(1):107-108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

