How reliable are ADC measurements? A phantom and clinical study of cervical lymph nodes
- PMID: 29476218
- PMCID: PMC6028847
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-017-5265-2
How reliable are ADC measurements? A phantom and clinical study of cervical lymph nodes
Abstract
Objective: To assess the reliability of ADC measurements in vitro and in cervical lymph nodes of healthy volunteers.
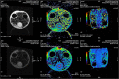
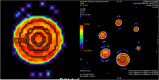
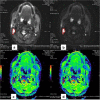
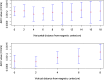
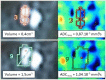
Methods: We used a GE 1.5 T MRI scanner and a first ice-water phantom according to recommendations released by the Quantitative Imaging Biomarker Alliance (QIBA) for assessing ADC against reference values. We analysed the target size effect by using a second phantom made of six inserted spheres with diameters ranging from 10 to 37 mm. Thirteen healthy volunteers were also scanned to assess the inter- and intra-observer reproducibility of volumetric ADC measurements of cervical lymph nodes.
Results: On the ice-water phantom, the error in ADC measurements was less than 4.3 %. The spatial bias due to the non-linearity of gradient fields was found to be 24 % at 8 cm from the isocentre. ADC measure reliability decreased when addressing small targets due to partial volume effects (up to 12.8 %). The mean ADC value of cervical lymph nodes was 0.87.10-3 ± 0.12.10-3 mm2/s with a good intra-observer reliability. Inter-observer reproducibility featured a bias of -5.5 % due to segmentation issues.
Conclusion: ADC is a potentially important imaging biomarker in oncology; however, variability issues preclude its broader adoption. Reliable use of ADC requires technical advances and systematic quality control.
Key points: • ADC is a promising quantitative imaging biomarker. • ADC has a fair inter-reader variability and good intra-reader variability. • Partial volume effect, post-processing software and non-linearity of scanners are limiting factors. • No threshold values for detecting cervical lymph node malignancy can be drawn.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Diffusion; Lymph; Magnetic resonance imaging; Quantitative evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Dr. Bastien Moreau, PhD.
Conflict of interest
Hubert Beaumont, as co-author of this manuscript, declares relationships with the following companies: Median Technologies.
All other authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
One of the authors has significant statistical expertise.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• prospective
• experimental
• performed at one institution
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

