Human Primary Cell-Based Organotypic Microtissues for Modeling Small Intestinal Drug Absorption
- PMID: 29476278
- PMCID: PMC6599640
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-018-2362-0
Human Primary Cell-Based Organotypic Microtissues for Modeling Small Intestinal Drug Absorption
Abstract
Purpose: The study evaluates the use of new in vitro primary human cell-based organotypic small intestinal (SMI) microtissues for predicting intestinal drug absorption and drug-drug interaction.
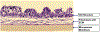
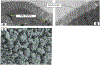
Methods: The SMI microtissues were reconstructed using human intestinal fibroblasts and enterocytes cultured on a permeable support. To evaluate the suitability of the intestinal microtissues to model drug absorption, the permeability coefficients across the microtissues were determined for a panel of 11 benchmark drugs with known human absorption and Caco-2 permeability data. Drug-drug interactions were examined using efflux transporter substrates and inhibitors.
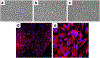
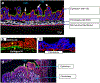
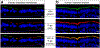
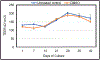
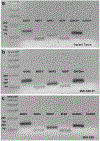
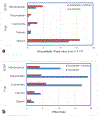
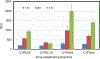
Results: The 3D-intestinal microtissues recapitulate the structural features and physiological barrier properties of the human small intestine. The microtissues also expressed drug transporters and metabolizing enzymes found on the intestinal wall. Functionally, the SMI microtissues were able to discriminate between low and high permeability drugs and correlated better with human absorption data (r2 = 0.91) compared to Caco-2 cells (r2 = 0.71). Finally, the functionality of efflux transporters was confirmed using efflux substrates and inhibitors which resulted in efflux ratios of >2.0 fold and by a decrease in efflux ratios following the addition of inhibitors.
Conclusion: The SMI microtissues appear to be a useful pre-clinical tool for predicting drug bioavailability of orally administered drugs.
Keywords: caco-2; drug metabolizing enzymes; drug permeation; drug transporters; drug-drug interaction; organotypic small intestinal microtissues.
Figures

References
-
- Loriot Y, Perlemuter G, Malka D, Penault-Llorca F, Boige V, Deutsch E, et al. Drug insight: gastrointestinal and hepatic adverse effects of molecular-targeted agents in cancer therapy. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2008;5:268–78. - PubMed
-
- Hubatsch I, Ragnarsson EGE, Artursson P. Determination of drug permeability and prediction of drug absorption in Caco-2 monolayers. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:2111–9. - PubMed
-
- Lee MKK, Dilq. Drug development in cell culture: crosstalk from the industrial prospects. J Bioequivalence Bioavailab. 2014;6:O96–O114.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

