Prognostic performance of serial in-hospital measurements of copeptin and multiple novel biomarkers among patients with worsening heart failure: results from the MOLITOR study
- PMID: 29476612
- PMCID: PMC5880673
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12231
Prognostic performance of serial in-hospital measurements of copeptin and multiple novel biomarkers among patients with worsening heart failure: results from the MOLITOR study
Abstract
Aims: In heart failure, various biomarkers are established for diagnosis and risk stratification; however, little is known about the relevance of serial measurements during an episode worsening heart failure (WHF). This study sought to investigate the trajectory of natriuretic peptides and multiple novel biomarkers during hospitalization for WHF and to determine the best time point to predict outcome.
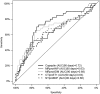
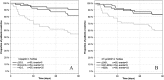
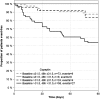
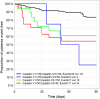
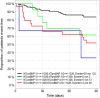
Methods and results: MOLITOR (Impact of Therapy Optimisation on the Level of Biomarkers in Patients with Acute and Decompensated Chronic Heart Failure) was an eight-centre prospective study of 164 patients hospitalized with a primary diagnosis of WHF. C-terminal fragment of pre-pro-vasopressin (copeptin), N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide (MR-proANP), mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-proADM), and C-terminal pro-endothelin-1 (CT-proET1) were measured on admission, after 24, 48, and 72 h, and every 72 h thereafter, at discharge and follow-up visits. Their performance to predict all-cause mortality and rehospitalization at 90 days was compared. All biomarkers decreased during recompensation (P < 0.05) except MR-proADM. Copeptin at admission was the best predictor of 90 day mortality or rehospitalization (χ2 = 16.63, C-index = 0.724, P < 0.001), followed by NT-proBNP (χ2 = 10.53, C-index = 0.646, P = 0.001), MR-proADM (χ2 = 9.29, C-index = 0.686, P = 0.002), MR-proANP (χ2 = 8.75, C-index = 0.631, P = 0.003), and CT-proET1 (χ2 = 6.60, C-index = 0.64, P = 0.010). Re-measurement of copeptin at 72 h and of NT-proBNP at 48 h increased prognostic value (χ2 = 23.48, C-index = 0.718, P = 0.00001; χ2 = 14.23, C-index = 0.650, P = 0.00081, respectively).
Conclusions: This largest sample of serial measurements of multiple biomarkers in WHF found copeptin at admission with re-measurement at 72 h to be the best predictor of 90 day mortality and rehospitalization.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01501981.
Keywords: Biomarker trajectory; Copeptin; Serial measurement; Worsening heart failure.
© 2018 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
References
-
- McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Böhm M, Dickstein K, Falk V, Filippatos G, Fonseca C, Gomez‐Sanchez MA, Jaarsma T, Køber L, Lip GY, Maggioni AP, Parkhomenko A, Pieske BM, Popescu BA, Rønnevik PK, Rutten FH, Schwitter J, Seferovic P, Stepinska J, Trindade PT, Voors AA, Zannad F, Zeiher A, Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology , Bax JJ, Baumgartner H, Ceconi C, Dean V, Deaton C, Fagard R, Funck‐Brentano C, Hasdai D, Hoes A, Kirchhof P, Knuuti J, Kolh P, McDonagh T, Moulin C, Popescu BA, Reiner Z, Sechtem U, Sirnes PA, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Vahanian A, Windecker S, McDonagh T, Sechtem U, Bonet LA, Avraamides P, Ben Lamin HA, Brignole M, Coca A, Cowburn P, Dargie H, Elliott P, Flachskampf FA, Guida GF, Hardman S, Iung B, Merkely B, Mueller C, Nanas JN, Nielsen OW, Orn S, Parissis JT, Ponikowski P, ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines . ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail 2012; 14: 803–869. - PubMed
-
- Maisel A, Mueller C, Nowak RM, Peacock WF, Ponikowski P, Mockel M, Hogan C, Wu AH, Richards M, Clopton P, Filippatos GS, Di Somma S, Anand I, Ng LL, Daniels LB, Neath SX, Christenson R, Potocki M, McCord J, Hartmann O, Morgenthaler NG, Anker SD. Midregion prohormone adrenomedullin and prognosis in patients presenting with acute dyspnea: results from the BACH (Biomarkers in Acute Heart Failure) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011; 58: 1057–1067. - PubMed
-
- Blanche P, Dartigues JF, Jacqmin‐Gadda H. Estimating and comparing time‐dependent areas under receiver operating characteristic curves for censored event times with competing risks. Stat Med 2013; 32: 5381–5397. - PubMed
-
- Hartmann O, Schuetz P, Albrich WC, Anker SD, Mueller B, Schmidt T. Time‐dependent Cox regression: serial measurement of the cardiovascular biomarker proadrenomedullin improves survival prediction in patients with lower respiratory tract infection. Int J Cardiol 2012; 161: 166–173. - PubMed
-
- Gegenhuber A, Struck J, Dieplinger B, Poelz W, Pacher R, Morgenthaler NG, Bergmann A, Haltmayer M, Mueller T. Comparative evaluation of B‐type natriuretic peptide, mid‐regional pro‐A‐type natriuretic peptide, mid‐regional pro‐adrenomedullin, and Copeptin to predict 1‐year mortality in patients with acute destabilized heart failure. J Card Fail 2007; 13: 42–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

