The Effort Paradox: Effort Is Both Costly and Valued
- PMID: 29477776
- PMCID: PMC6172040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tics.2018.01.007
The Effort Paradox: Effort Is Both Costly and Valued
Abstract
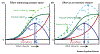
According to prominent models in cognitive psychology, neuroscience, and economics, effort (be it physical or mental) is costly: when given a choice, humans and non-human animals alike tend to avoid effort. Here, we suggest that the opposite is also true and review extensive evidence that effort can also add value. Not only can the same outcomes be more rewarding if we apply more (not less) effort, sometimes we select options precisely because they require effort. Given the increasing recognition of effort's role in motivation, cognitive control, and value-based decision-making, considering this neglected side of effort will not only improve formal computational models, but also provide clues about how to promote sustained mental effort across time.
Keywords: cognitive control; cognitive dissonance; decision-making; effort; learned industriousness; need for cognition; value.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Kurzban R (2016) T0068e sense of effort. Curr. Opin. Psychol 7, 67–70
-
- Dreisbach G and Fischer R (2015) Conflicts as aversive sig-nals for control adaptation. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci 24, 255–260
-
- Saunders B et al. (2016) The emotive nature of conflict moni-toring in the medial prefrontal cortex. Int. J. Psychophysiol 119, 31–40 - PubMed
-
- Frederick S (2005) Cognitive reflection and decision making. J. Econ. Perspect 19, 25–42
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

