Patient-Reported Outcomes in Relation to Continuously Monitored Rhythm Before and During 2 Years After Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Using a Disease-Specific and a Generic Instrument
- PMID: 29478027
- PMCID: PMC5866340
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.008362
Patient-Reported Outcomes in Relation to Continuously Monitored Rhythm Before and During 2 Years After Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Using a Disease-Specific and a Generic Instrument
Abstract
Background: Atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation improves patient-reported outcomes, irrespective of mode of intermittent rhythm monitoring. We evaluated the use of an AF-specific and a generic patient-reported outcomes instrument during continuous rhythm monitoring 2 years after AF ablation.
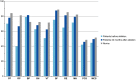
Methods and results: Fifty-four patients completed the generic 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey and the AF-specific AF6 questionnaires before and 6, 12, and 24 months after AF ablation. All patients underwent continuous ECG monitoring via an implantable loop recorder. The generic patient-reported outcomes scores were compared with those of a Swedish age- and sex-matched population. After ablation, both summary scores reached normative levels at 24 months, while role-physical and vitality remained lower than norms. Responders to ablation (AF burden <0.5%) reached the norms in all individual 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey domains, while nonresponders (AF burden >0.5%) reached norms only in social functioning and mental component summary. All AF6 items and the sum score showed moderate to large improvement in both responders and nonresponders, although responders showed significantly greater improvement in all items except item 1 from before to 24 months after ablation. Higher AF burden was independently associated with poorer physical component summary and AF6 sum score.
Conclusions: The AF-specific AF6 questionnaire was more sensitive to changes related to AF burden than the generic 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey. Patients improved as documented by both instruments, but a higher AF burden after ablation was associated with poorer AF-specific patient-reported outcomes and poorer generic physical but not mental health. Our results support the use of an AF-specific instrument, alone or in combination with a generic instrument, to assess the effect of ablation.
Clinical trial registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00697359.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; catheter ablation; quality of life.
© 2018 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures
References
-
- Dorian P, Jung W, Newman D, Paquette M, Wood K, Ayers GM, Camm J, Akhtar M, Luderitz B. The impairment of health‐related quality of life in patients with intermittent atrial fibrillation: implications for the assessment of investigational therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:1303–1309. - PubMed
-
- Hagens VE, Ranchor AV, Van Sonderen E, Bosker HA, Kamp O, Tijssen JG, Kingma JH, Crijns HJ, Van Gelder IC. Effect of rate or rhythm control on quality of life in persistent atrial fibrillation. Results from the Rate Control Versus Electrical Cardioversion (RACE) Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:241–247. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds MR, Lavelle T, Essebag V, Cohen DJ, Zimetbaum P. Influence of age, sex, and atrial fibrillation recurrence on quality of life outcomes in a population of patients with new‐onset atrial fibrillation: the Fibrillation Registry Assessing Costs, Therapies, Adverse events and Lifestyle (FRACTAL) study. Am Heart J. 2006;152:1097–1103. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B, Castella M, Diener HC, Heidbuchel H, Hendriks J, Hindricks G, Manolis AS, Oldgren J, Popescu BA, Schotten U, Van Putte B, Vardas P, Agewall S, Camm J, Baron Esquivias G, Budts W, Carerj S, Casselman F, Coca A, De Caterina R, Deftereos S, Dobrev D, Ferro JM, Filippatos G, Fitzsimons D, Gorenek B, Guenoun M, Hohnloser SH, Kolh P, Lip GY, Manolis A, McMurray J, Ponikowski P, Rosenhek R, Ruschitzka F, Savelieva I, Sharma S, Suwalski P, Tamargo JL, Taylor CJ, Van Gelder IC, Voors AA, Windecker S, Zamorano JL, Zeppenfeld K. 2016 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Europace. 2016;18:1609–1678. - PubMed
-
- Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, Kim YH, Saad EB, Aguinaga L, Akar JG, Badhwar V, Brugada J, Camm J, Chen PS, Chen SA, Chung MK, Nielsen JC, Curtis AB, Davies DW, Day JD, d'Avila A, de Groot N, Di Biase L, Duytschaever M, Edgerton JR, Ellenbogen KA, Ellinor PT, Ernst S, Fenelon G, Gerstenfeld EP, Haines DE, Haissaguerre M, Helm RH, Hylek E, Jackman WM, Jalife J, Kalman JM, Kautzner J, Kottkamp H, Kuck KH, Kumagai K, Lee R, Lewalter T, Lindsay BD, Macle L, Mansour M, Marchlinski FE, Michaud GF, Nakagawa H, Natale A, Nattel S, Okumura K, Packer D, Pokushalov E, Reynolds MR, Sanders P, Scanavacca M, Schilling R, Tondo C, Tsao HM, Verma A, Wilber DJ, Yamane T. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14:e275–e444. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

