Feasibility and reliability of frailty assessment in the critically ill: a systematic review
- PMID: 29478414
- PMCID: PMC6389132
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-018-1953-9
Feasibility and reliability of frailty assessment in the critically ill: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: For healthcare systems, an ageing population poses challenges in the delivery of equitable and effective care. Frailty assessment has the potential to improve care in the intensive care setting, but applying assessment tools in critical illness may be problematic. The aim of this systematic review was to evaluate evidence for the feasibility and reliability of frailty assessment in critical care.
Methods: Our primary search was conducted in Medline, Medline In-process, EMBASE, CINAHL, PsycINFO, AMED, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and Web of Science (January 2001 to October 2017). We included observational studies reporting data on feasibility and reliability of frailty assessment in the critical care setting in patients 16 years and older. Feasibility was assessed in terms of timing of evaluation, the background, training and expertise required for assessors, and reliance upon proxy input. Reliability was assessed in terms of inter-rater reliability.
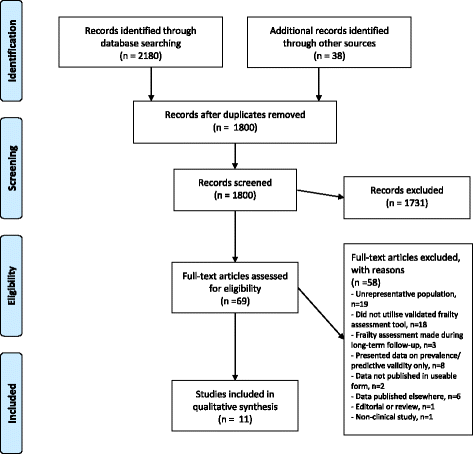
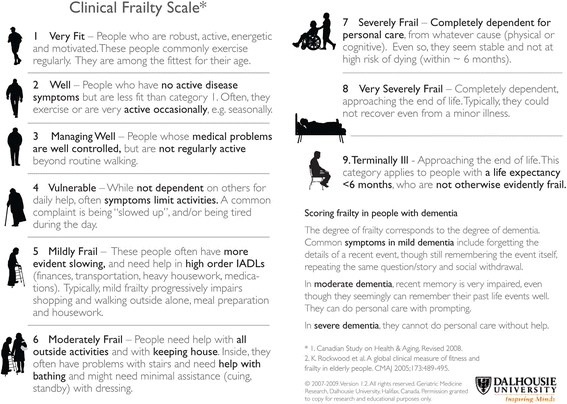
Results: Data from 11 study publications are included, representing 8 study cohorts and 7761 patients. Proxy involvement in frailty assessment ranged from 58 to 100%. Feasibility data were not well-reported overall, but the exclusion rate due to lack of proxy availability ranged from 0 to 45%, the highest rate observed where family involvement was mandatory and the assessment tool relatively complex (frailty index, FI). Conventional elements of frailty phenotype (FP) assessment required modification prior to use in two studies. Clinical staff tended to use a simple judgement-based tool, the clinical frailty scale (CFS). Inter-rater reliability was reported in one study using the CFS and although a good level of agreement was observed between clinician assessments, this was a small and single-centre study.
Conclusion: Though of unproven reliability in the critically ill, CFS was the tool used most widely by critical care clinical staff. Conventional FP assessment required modification for general application in critical care, and an FI-based assessment may be difficult to deliver by the critical care team on a routine basis. There is a high reliance on proxies for frailty assessment, and the reliability of frailty assessment tools in critical care needs further evaluation.
Prospero registration number: CRD42016052073 .
Keywords: Clinical frailty scale; Critical care; Critically ill; Feasibility; Frailty; Frailty Index; Frailty phenotype; Intensive care; Reliability.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical