Genome-wide Association Study Identifies a Regulatory Variant of RGMA Associated With Opioid Dependence in European Americans
- PMID: 29478698
- PMCID: PMC6041180
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.12.016
Genome-wide Association Study Identifies a Regulatory Variant of RGMA Associated With Opioid Dependence in European Americans
Abstract
Background: Opioid dependence (OD) is at epidemic levels in the United States. Genetic studies can provide insight into its biology.
Methods: We completed an OD genome-wide association study in 3058 opioid-exposed European Americans, 1290 of whom met criteria for a DSM-IV diagnosis of OD. Analysis used DSM-IV criterion count.
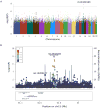
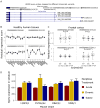
Results: By meta-analysis of four cohorts, Yale-Penn 1 (n = 1388), Yale-Penn 2 (n = 996), Yale-Penn 3 (n = 98), and SAGE (Study of Addiction: Genetics and Environment) (n = 576), we identified a variant on chromosome 15, rs12442183, near RGMA, associated with OD (p = 1.3 × 10-8). The association was also genome-wide significant in Yale-Penn 1 taken individually and nominally significant in two of the other three samples. The finding was further supported in a meta-analysis of all available opioid-exposed African Americans (n = 2014 [1106 meeting DSM-IV OD criteria]; p = 3.0 × 10-3) from three cohorts; there was nominal significance in two of these samples. Thus, of seven subsamples examined in two populations, one was genome-wide significant, and four of six were nominally (or nearly) significant. RGMA encodes repulsive guidance molecule A, which is a central nervous system axon guidance protein. Risk allele rs12442183*T was correlated with higher expression of a specific RGMA transcript variant in frontal cortex (p = 2 × 10-3). After chronic morphine injection, the homologous mouse gene (Rgma) was upregulated in C57BL/6J striatum. Coexpression analysis of 1301 brain samples revealed that RGMA messenger RNA expression was associated with that of four genes implicated in other psychiatric disorders, including GRIN1.
Conclusions: This is the first study to demonstrate an association of RGMA with OD. It provides a new lead into our understanding of OD pathophysiology.
Keywords: European Americans; Genome-wide association; Opioid dependence; Psychiatric genetics; RGMA; Regulatory variant.
Copyright © 2018 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

