Efficacy of minimally invasive surfactant therapy in moderate and late preterm infants: A multicentre randomized control trial
- PMID: 29479196
- PMCID: PMC5804903
- DOI: 10.1093/pch/pxx033
Efficacy of minimally invasive surfactant therapy in moderate and late preterm infants: A multicentre randomized control trial
Abstract
Background: Minimally invasive surfactant therapy (MIST) is a new strategy to avoid mechanical ventilation (MV) in respiratory distress syndrome. The primary aim of this study was to test MIST as a means of avoiding MV exposure and pneumothorax occurrence in moderate and late preterm infants (32 to 36 weeks' gestational age).
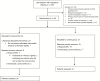
Methods: This was a randomized controlled trial including three Canadian centres. Patients were randomized to standard management or to the intervention if they required nasal continuous positive airway pressure of 6 cm H2O and 35% FiO2 in the first 24 hours of life. Patients from the intervention group received MIST immediately after inclusion. The primary outcome was either need for MV or development of a pneumothorax requiring a chest tube. To ensure that clinicians were not biased toward delaying intubation in the intervention group, clinical failure criteria were also used as a primary outcome. The primary outcome was analyzed using bivariate and multivariate logistic regressions.
Results: Among 45 randomized patients, 24 were assigned to MIST and 21 to standard management. Eight infants (33%) from the intervention group met the primary outcome criteria versus 19 (90%) in the control group (absolute risk reduction 0.57, 95% confidence interval 0.54 to 0.60). One patient in each group reached the primary outcome because of pneumothorax occurrence. The other patients were exposed to MV. None of the patients reached the clinical failure criteria.
Conclusion: MIST for respiratory distress syndrome management in moderate and late preterm infants was associated with a significant reduction of MV exposure and pneumothorax occurrence.
Keywords: Hyaline membrane disease; Infant; Premature; Pulmonary surfactants; Respiratory distress syndrome; Spontaneous breathing..
Figures
References
-
- Hamilton BE, Martin JA, Ventura SJ. Births: Preliminary data for 2006. Natl Vital Stat Rep 2007;56:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Bassil KL, Shah PS, Shah V, Ye XY, Lee SK, Jefferies AL; Canadian Neonatal Network Impact of late preterm and early term infants on Canadian neonatal intensive care units. Am J Perinatol 2014;31:269–78. - PubMed
-
- Teune MJ, Bakhuizen S, Gyamfi Bannerman C, et al. A systematic review of severe morbidity in infants born late preterm. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;205:374.e1–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
