Deep sequencing and in silico analysis of small RNA library reveals novel miRNA from leaf Persicaria minor transcriptome
- PMID: 29479512
- PMCID: PMC5814390
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-018-1164-8
Deep sequencing and in silico analysis of small RNA library reveals novel miRNA from leaf Persicaria minor transcriptome
Abstract
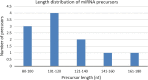
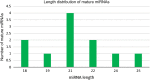
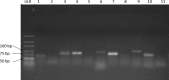
In current era, majority of microRNA (miRNA) are being discovered through computational approaches which are more confined towards model plants. Here, for the first time, we have described the identification and characterization of novel miRNA in a non-model plant, Persicaria minor (P. minor) using computational approach. Unannotated sequences from deep sequencing were analyzed based on previous well-established parameters. Around 24 putative novel miRNAs were identified from 6,417,780 reads of the unannotated sequence which represented 11 unique putative miRNA sequences. PsRobot target prediction tool was deployed to identify the target transcripts of putative novel miRNAs. Most of the predicted target transcripts (mRNAs) were known to be involved in plant development and stress responses. Gene ontology showed that majority of the putative novel miRNA targets involved in cellular component (69.07%), followed by molecular function (30.08%) and biological process (0.85%). Out of 11 unique putative miRNAs, 7 miRNAs were validated through semi-quantitative PCR. These novel miRNAs discoveries in P. minor may develop and update the current public miRNA database.
Keywords: Deep sequencing; In silico; Novel miRNA; Persicaria minor; Transcriptomic library.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThere are no conflicts to declare by authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of terpenoid biosynthesis by miRNA in Persicaria minor induced by Fusarium oxysporum.BMC Genomics. 2019 Jul 16;20(1):586. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5954-0. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31311515 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Taxus microRNAs and their targets with high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis.Physiol Plant. 2012 Dec;146(4):388-403. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01668.x. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Physiol Plant. 2012. PMID: 22708792
-
MicroRNA profiling of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci Middle East-Aisa Minor I following the acquisition of Tomato yellow leaf curl China virus.Virol J. 2016 Feb 2;13:20. doi: 10.1186/s12985-016-0469-7. Virol J. 2016. PMID: 26837429 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Machine Learning in miRNA Discovery and Target Prediction.Curr Genomics. 2019 Dec;20(8):537-544. doi: 10.2174/1389202921666200106111813. Curr Genomics. 2019. PMID: 32581642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methods in molecular cardiology: in silico cloning.Neth Heart J. 2004 Sep;12(9):400-403. Neth Heart J. 2004. PMID: 25696371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of miRNA-mediated fertility regulation network of cytoplasmic male sterility during flower bud development in soybean.3 Biotech. 2019 Jan;9(1):22. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1543-1. Epub 2019 Jan 2. 3 Biotech. 2019. PMID: 30622860 Free PMC article.
-
Functional annotation of differentially expressed fetal cardiac microRNA targets: implication for microRNA-based cardiovascular therapeutics.3 Biotech. 2018 Dec;8(12):494. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1520-8. Epub 2018 Nov 21. 3 Biotech. 2018. PMID: 30498667 Free PMC article.
-
Christia vespertilionis extract induced antiproliferation and apoptosis in breast cancer (MCF7) cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Nov;48(11):7361-7370. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06743-w. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34665399
-
In silico identification of conserved miRNAs and their selective target gene prediction in indicine (Bos indicus) cattle.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 26;13(10):e0206154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206154. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30365525 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-mediated bioengineering for climate-resilience in crops.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):10430-10456. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1997244. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34747296 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

