Delineating Crosstalk Mechanisms of the Ubiquitin Proteasome System That Regulate Apoptosis
- PMID: 29479529
- PMCID: PMC5811474
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00011
Delineating Crosstalk Mechanisms of the Ubiquitin Proteasome System That Regulate Apoptosis
Abstract
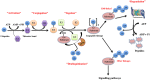
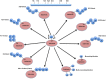
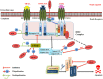
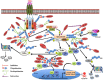
Regulatory functions of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) are exercised mainly by the ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinating enzymes. Degradation of apoptotic proteins by UPS is central to the maintenance of cell health, and deregulation of this process is associated with several diseases including tumors, neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, and inflammation. Therefore, it is the view that interrogating protein turnover in cells can offer a strategy for delineating disease-causing mechanistic perturbations and facilitate identification of drug targets. In this review, we are summarizing an overview to elucidate the updated knowledge on the molecular interplay between the apoptosis and UPS pathways. We have condensed around 100 enzymes of UPS machinery from the literature that ubiquitinates or deubiquitinates the apoptotic proteins and regulates the cell fate. We have also provided a detailed insight into how the UPS proteins are able to fine-tune the intrinsic, extrinsic, and p53-mediated apoptotic pathways to regulate cell survival or cell death. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the potential of UPS players as a drug target for cancer and other human disorders.
Keywords: DUBs; E3 ligases; apoptosis; ubiquitin proteasome system; ubiquitination.
Figures

Similar articles
-
E3 ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases as modulators of TRAIL-mediated extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway.BMB Rep. 2019 Feb;52(2):119-126. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.2.011. BMB Rep. 2019. PMID: 30638181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway by Natural Products: Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Physiol. 2020 Apr 28;11:361. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00361. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32411012 Free PMC article.
-
The potential roles of deubiquitinating enzymes in brain diseases.Ageing Res Rev. 2020 Aug;61:101088. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101088. Epub 2020 May 26. Ageing Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 32470641 Review.
-
Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in brain ischemia: friend or foe?Prog Neurobiol. 2014 Jan;112:50-69. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.10.003. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Prog Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24157661 Review.
-
Hidden targets of ubiquitin proteasome system: To prevent diabetic nephropathy.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Jun;120:170-179. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.03.024. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28363724 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural and Designed Proteins Inspired by Extremotolerant Organisms Can Form Condensates and Attenuate Apoptosis in Human Cells.ACS Synth Biol. 2022 Mar 18;11(3):1292-1302. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.1c00572. Epub 2022 Feb 18. ACS Synth Biol. 2022. PMID: 35176859 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of neddylation modification by MLN4924 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib.Oncol Rep. 2019 Jun;41(6):3257-3269. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7098. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Oncol Rep. 2019. Retraction in: Oncol Rep. 2025 Mar;53(3):33. doi: 10.3892/or.2025.8866. PMID: 31002342 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Roles of ubiquitin in autophagy and cell death.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Sep;93:125-135. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30195063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dual functions of α-tubulin acetylation in cellular apoptosis and autophage induced by tanespimycin in lung cancer cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Aug 5;20:369. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01453-y. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32774163 Free PMC article.
-
Deubiquitinating Enzymes and Bone Remodeling.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Jul 8;2018:3712083. doi: 10.1155/2018/3712083. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 30123285 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

