Correlation between the pronucleus size and the potential for human single pronucleus zygotes to develop into blastocysts : 1PN zygotes with large pronuclei can expect an embryo development to the blastocyst stage that is similar to the development of 2PN zygotes
- PMID: 29479641
- PMCID: PMC5984884
- DOI: 10.1007/s10815-018-1137-1
Correlation between the pronucleus size and the potential for human single pronucleus zygotes to develop into blastocysts : 1PN zygotes with large pronuclei can expect an embryo development to the blastocyst stage that is similar to the development of 2PN zygotes
Abstract
Purpose: In this study, we examined the correlation between pronucleus size and the potential for human single pronucleus (1PN) zygotes to develop into blastocysts after IVF and ICSI.
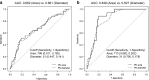
Methods: This study included 112 patients who underwent a total of 112 cycles of IVF/ICSI. To evaluate embryo development, 1PN zygotes were compared with 2PN zygotes in the same IVF/ICSI cycle (control cycles) using time-lapse live embryo imaging. To assess the potential for blastocyst formation, cutoff values for pronuclear area and diameter were established through receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, after which 1PN zygotes were classified based on those cutoff values.
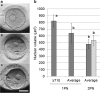
Results: Among 1PN zygotes cultured to day 5/6, the rate of embryo development was significantly lower than from 2PN zygotes. However, the rates of blastocyst formation and good quality blastocysts from 1PN zygotes with large pronuclear areas (≥ 710 μm2) or diameters (≥ 31 μm) were significantly higher than from 1PN zygotes with smaller pronuclear areas (≤ 509, 510-609, and 610-709 μm2) or diameters (≤ 24, 25-27,and 28-30 μm) (P < 0.01). Moreover, the results for 1PN zygotes with large pronuclei were similar to those for 2PN zygotes.
Conclusions: The developmental potential of 1PN zygotes with large pronuclear areas (≥ 710 μm2) or diameters (31 μm) appears to be similar to that of 2PN zygotes, and measurement of pronuclear area or diameter in 1PN zygotes is a simple, potentially useful, clinical method.
Keywords: Blastocyst culture; ICSI; IVF; Pronucleus size; Single pronucleus zygotes; Time-lapse live embryo imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kishokai Medical Corporation and was conducted in accordance with the principals expressed in the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients provided consent to all treatment procedures and agreed to anonymous use of their data for studies.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

