Expression of Laminin in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas
- PMID: 29479990
- PMCID: PMC5980927
- DOI: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.2.407
Expression of Laminin in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Abstract
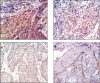
Background and objectives: Laminin is a significant basement membrane (BM) glycoprotein, the expression of which reflects BM integrity more precisely than do other ECM proteins. The present study aimed to evaluate laminin expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas OSCC and to determine any associations with clinico-pathological parameters (surgical margin status, lymph node involvement, survival and recurrence). Methods: Laminin expression was evaluated in 31 cases of biopsy-proven OSCC by immunohistochemical staining and its association with prognosticators and the Brynes grading system was determined by appropriate statistical analysis. Results: We observed a significant increase in linear staining pattern (p<0.001) at the tumour-host interface in well-differentiated OSCC cases, in contrast to poorly differentiated lesions which exhibited intense cytoplasmic expression within tumour cells. Higher cytoplasmic laminin expression was seen in 33.3% of cases with involved surgical margins and 69.2% of cases with lymph node metastasis (along with weak/absent staining of laminin around the tumour-host interface – Basement membrane around tumour islands). Similarly, in 60% of the cases who died and in 81.8% of cases with tumour recurrence, moderately intense cytoplasmic laminin expression was seen within tumour cells. On comparing variables of the Brynes grading system, significant cytoplasmic expression of laminin was linked with mild inflammation (p<0.0016) and increased mitotic activity (p<0.008). Conclusion: Based on these observations, immunohistochemical expression of laminin might be useful to evaluate histological differentiation and aggressiveness of OSCCs.
Keywords: Laminin; basement membrane; OSCC; prognosis.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures

Similar articles
-
A correlation of immunohistochemical expression of TP53 and CDKN1A in oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Ther. 2018 Apr-Jun;14(3):666-670. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.180683. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29893337
-
High HMGA2 Expression Correlates with Reduced Recurrence-free Survival and Poor Overall Survival in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2017 Apr;37(4):1891-1899. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11527. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28373457
-
[The relationship between expression of basement membrane in squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity and cervical lymph node metastasis].Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 1997;22(1):41-4. Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 1997. PMID: 9868026 Chinese.
-
P-cadherin expression predicts clinical outcome in oral squamous cell carcinomas.Histol Histopathol. 2004 Oct;19(4):1089-99. doi: 10.14670/HH-19.1089. Histol Histopathol. 2004. PMID: 15375751
-
Use of basement membrane markers in tumour diagnosis.J Clin Pathol. 1989 May;42(5):449-57. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.5.449. J Clin Pathol. 1989. PMID: 2659627 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The tumor ecosystem in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and advances in ecotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2023 Apr 6;22(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01769-z. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37024932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orchestrated expression of vasculogenic mimicry and laminin-5γ2 is an independent prognostic marker in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Exp Pathol. 2022 Apr;103(2):54-64. doi: 10.1111/iep.12430. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Int J Exp Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35170826 Free PMC article.
-
Hyalinization as a histomorphological risk predictor in oral pathological lesions.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021 Jul-Sep;11(3):415-422. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.05.002. Epub 2021 May 20. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021. PMID: 34094841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Laminin Immunostaining in Biopsies as a Useful Biomarker of Early Invasion in Actinic Cheilitis and Differential Diagnosis Between Actinic Cheilitis and Lip Cancer: New Insights.Head Neck Pathol. 2023 Jun;17(2):331-338. doi: 10.1007/s12105-022-01504-y. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Head Neck Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36303015 Free PMC article.
-
ECM Remodeling in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Aerodigestive Tract: Pathways for Cancer Dissemination and Emerging Biomarkers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 2;13(11):2759. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112759. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34199373 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arduino PG, Carrozzo M, Pagano M, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of basement membrane proteins of verrucous carcinoma of the oral mucosa. Clin Oral Invest. 2010;14:297–302. - PubMed
-
- Corbalan-Velez R, Martínez-Barba E, Lopez-Poveda MJ, et al. The value of laminin 322 staining in distinguishing between keratoacanthoma, keratoacanthoma with areas of squamous cell carcinoma, and crateriform squamous cell carcinoma. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2012;103:308–16. - PubMed
-
- Fitsialos G, Bourget I, Augier S, et al. HIF1 transcription factor regulates laminin-332 expression and keratinocyte migration. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:2992–3001. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

