Myosin light chain kinase ( MYLK) coding polymorphisms modulate human lung endothelial cell barrier responses via altered tyrosine phosphorylation, spatial localization, and lamellipodial protrusions
- PMID: 29480069
- PMCID: PMC5846938
- DOI: 10.1177/2045894018764171
Myosin light chain kinase ( MYLK) coding polymorphisms modulate human lung endothelial cell barrier responses via altered tyrosine phosphorylation, spatial localization, and lamellipodial protrusions
Abstract
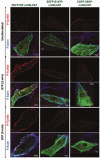
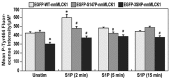
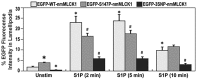
Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) is a potent bioactive endogenous lipid that signals a rearrangement of the actin cytoskeleton via the regulation of non-muscle myosin light chain kinase isoform (nmMLCK). S1P induces critical nmMLCK Y464 and Y471 phosphorylation resulting in translocation of nmMLCK to the periphery where spatially-directed increases in myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation and tension result in lamellipodia protrusion, increased cell-cell adhesion, and enhanced vascular barrier integrity. MYLK, the gene encoding nmMLCK, is a known candidate gene in lung inflammatory diseases, with coding genetic variants (Pro21His, Ser147Pro, Val261Ala) that confer risk for inflammatory lung injury and influence disease severity. The functional mechanisms by which these MYLK coding single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) affect biologic processes to increase disease risk and severity remain elusive. In the current study, we utilized quantifiable cell immunofluorescence assays to determine the influence of MYLK coding SNPs on S1P-mediated nmMLCK phosphorylation and translocation to the human lung endothelial cell (EC) periphery . These disease-associated MYLK variants result in reduced levels of S1P-induced Y464 phosphorylation, a key site for nmMLCK enzymatic regulation and activation. Reduced Y464 phosphorylation resulted in attenuated nmMLCK protein translocation to the cell periphery. We further conducted EC kymographic assays which confirmed that lamellipodial protrusion in response to S1P challenge was retarded by expression of a MYLK transgene harboring the three MYLK coding SNPs. These data suggest that ARDS/severe asthma-associated MYLK SNPs functionally influence vascular barrier-regulatory cytoskeletal responses via direct alterations in the levels of nmMLCK tyrosine phosphorylation, spatial localization, and lamellipodial protrusions.
Keywords: S1P; SNP; nmMLCK; sphingosine 1-phosphate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Abl tyrosine kinase phosphorylates nonmuscle Myosin light chain kinase to regulate endothelial barrier function.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Nov 15;21(22):4042-56. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E09-10-0876. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20861316 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 activation induces inflammatory vascular permeability via Dock1 targeting and NOX4 upregulation.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022 Dec 1;1868(12):166562. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166562. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022. PMID: 36179995 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative distribution and colocalization of non-muscle myosin light chain kinase isoforms and cortactin in human lung endothelium.Microvasc Res. 2010 Jul;80(1):75-88. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2009.12.010. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Microvasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20053363 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cortical Actin Dynamics in Endothelial Permeability.Curr Top Membr. 2018;82:141-195. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Curr Top Membr. 2018. PMID: 30360779 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and epigenetic regulation of the non-muscle myosin light chain kinase isoform by lung inflammatory factors and mechanical stress.Clin Sci (Lond). 2021 Apr 16;135(7):963-977. doi: 10.1042/CS20201448. Clin Sci (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33792658 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mechanisms regulating endothelial barrier function in the pulmonary microcirculation.J Physiol. 2019 Feb;597(4):997-1021. doi: 10.1113/JP276245. Epub 2018 Aug 13. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30015354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Splicing Factor hnRNPA1 Regulates Alternate Splicing of the MYLK Gene.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018 May;58(5):604-613. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0141OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29077485 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal dynamics of the multi-omic response to endurance exercise training.Nature. 2024 May;629(8010):174-183. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06877-w. Epub 2024 May 1. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38693412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lazar V, Garcia JG. A single human myosin light chain kinase gene (MLCK; MYLK). Genomics 1999; 57(2): 256–267. - PubMed
-
- Garcia JG, Davis HW, Patterson CE. Regulation of endothelial cell gap formation and barrier dysfunction: role of myosin light chain phosphorylation. J Cell Physiol 1995; 163(3): 510–522. - PubMed
-
- Davis HW, Crimmins DL, Thoma RS, et al. Phosphorylation of calmodulin in the first calcium-binding pocket by myosin light chain kinase. Arch Biochem Biophys 1996; 332(1): 101–109. - PubMed
-
- Garcia JG, Verin AD, Schaphorst K, et al. Regulation of endothelial cell myosin light chain kinase by Rho, cortactin, and p60(src). Am J Physiol 1999; 276(6 Pt 1): L989–998. - PubMed
-
- Birukov KG, Csortos C, Marzilli L, et al. Differential regulation of alternatively spliced endothelial cell myosin light chain kinase isoforms by p60(Src). J Biol Chem 2001; 276(11): 8567–8573. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

