Translational repression of HIF2α expression in mice with Chuvash polycythemia reverses polycythemia
- PMID: 29480820
- PMCID: PMC5873849
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI97684
Translational repression of HIF2α expression in mice with Chuvash polycythemia reverses polycythemia
Abstract
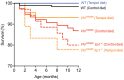
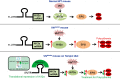
Chuvash polycythemia is an inherited disease caused by a homozygous germline VHLR200W mutation, which leads to impaired degradation of HIF2α, elevated levels of serum erythropoietin, and erythrocytosis/polycythemia. This phenotype is recapitulated by a mouse model bearing a homozygous VhlR200W mutation. We previously showed that iron-regulatory protein 1-knockout (Irp1-knockout) mice developed erythrocytosis/polycythemia through translational derepression of Hif2α, suggesting that IRP1 could be a therapeutic target to treat Chuvash polycythemia. Here, we fed VhlR200W mice supplemented with Tempol, a small, stable nitroxide molecule and observed that Tempol decreased erythropoietin production, corrected splenomegaly, normalized hematocrit levels, and increased the lifespans of these mice. We attribute the reversal of erythrocytosis/polycythemia to translational repression of Hif2α expression by Tempol-mediated increases in the IRE-binding activity of Irp1, as reversal of polycythemia was abrogated in VhlR200W mice in which Irp1 was genetically ablated. Thus, a new approach to the treatment of patients with Chuvash polycythemia may include dietary supplementation of Tempol, which decreased Hif2α expression and markedly reduced life-threatening erythrocytosis/polycythemia in the VhlR200W mice.
Keywords: Drug therapy; Hematology; Pharmacology; Translation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
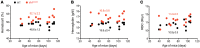
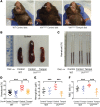
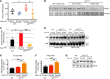
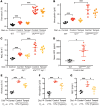
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

