Melanoma Screening Day in Krasnoyarsk Krai of the Russian Federation: Results from 2015-2016
- PMID: 29480992
- PMCID: PMC5980941
- DOI: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.2.503
Melanoma Screening Day in Krasnoyarsk Krai of the Russian Federation: Results from 2015-2016
Abstract
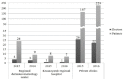
Objective: The Melanoma Screening Day Campaign started in the Russian Federation in 2006. In the present study, we analyzed the 2015-2016 survey questionnaire data acquired from screened individuals in the city of Krasnoyarsk in eastern Siberia, which has a population of one million, in order to understand the level of awareness regarding melanoma/ skin cancer prevention and early diagnosis. Methods: Individuals were enrolled in the screening campaign by mass media advertising. Free whole-body examinations were provided by the doctors, and the standardized questionnaire forms (n=444) were completed to obtain relevant demographic, epidemiological, and clinical data. Descriptive and univariate analyses were conducted to elucidate the main characteristics of the screened population. Percentage frequency was used to characterize the population. Result: A substantial proportion of the screened individuals were female (80%). The most common reasons for participating in the screening were a high number of moles, or a change in the appearance of the moles. Internet recourses were the main channel for obtaining the information about the Melanoma Day Screening Campaign. 5% of screened individuals had a family history of melanoma/skin cancer. The mean age of the participants was 36.63±16.31 years. The percentage of screened individuals who took part in this program increased in 2016 (18%) versus 2015 (8%). In total, 5 individuals with suspected melanoma/skin cancer were identified during the two-year Campaign, all of whom were referred to the regional oncology center. Conclusion: The analysis of data from the Melanoma Screening Day Campaign in Krasnoyarsk Krai revealed the necessity to use the media to attract older subjects with potential melanoma/skin cancer risk to undergo screening. Individuals with suspected malignancies should be monitored up until the time when a final diagnosis is determined. Moreover, such events are an appropriate way to inform and educate the public about cutaneous cancer prevention.
Keywords: Melanoma; nevi; screening; Siberia; Russian Federation.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures
References
-
- Kaprin AD, Starinskiy VV, Petrova GV. Malignancies in Russia in 2014 (morbidity and mortality) Moscow: RIIS FIAN; 2015. p. 249. (in Russian)
-
- Kelly JW, Yeatman JM, Regalia C, et al. A high incidence of melanoma found in patients with multiple dysplastic naevi using photographic surveillance. Med J Aust. 1997;167:191–4. - PubMed
-
- Kiellberg LH, Sand C. Referral pattern of skin diseases in an acute outpatient dermatological clinic in Copenhagen. Acta Derm Venereol. 2005;85:509–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical