Turnover of aberrant pre-40S pre-ribosomal particles is initiated by a novel endonucleolytic decay pathway
- PMID: 29481617
- PMCID: PMC5961177
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky116
Turnover of aberrant pre-40S pre-ribosomal particles is initiated by a novel endonucleolytic decay pathway
Abstract
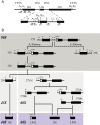
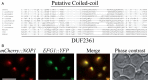
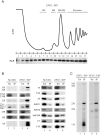
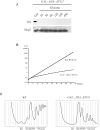
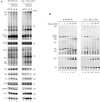
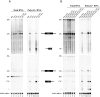
Ribosome biogenesis requires more than 200 trans-acting factors to achieve the correct production of the two mature ribosomal subunits. Here, we have identified Efg1 as a novel, nucleolar ribosome biogenesis factor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae that is directly linked to the surveillance of pre-40S particles. Depletion of Efg1 impairs early pre-rRNA processing, leading to a strong decrease in 18S rRNA and 40S subunit levels and an accumulation of the aberrant 23S rRNA. Using Efg1 as bait, we revealed a novel degradation pathway of the 23S rRNA. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments showed that Efg1 is a component of 90S pre-ribosomes, as it is associated with the 35S pre-rRNA and U3 snoRNA, but has stronger affinity for 23S pre-rRNA and its novel degradation intermediate 11S rRNA. 23S is cleaved at a new site, Q1, within the 18S sequence by the endonuclease Utp24, generating 11S and 17S' rRNA. Both of these cleavage products are targeted for degradation by the TRAMP/exosome complexes. Therefore, the Q1 site defines a novel endonucleolytic cleavage site of ribosomal RNA exclusively dedicated to surveillance of pre-ribosomal particles.
Figures


References
-
- Grandi P., Rybin V., Bassler J., Petfalski E., Strauss D., Marzioch M., Schafer T., Kuster B., Tschochner H., Tollervey D. et al. . 90S pre-ribosomes include the 35S pre-rRNA, the U3 snoRNP, and 40S subunit processing factors but predominantly lack 60S synthesis factors. Mol. Cell. 2002; 10:105–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

