Two-Year Outcomes of Sacral Neuromodulation Versus OnabotulinumtoxinA for Refractory Urgency Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Trial
- PMID: 29482936
- PMCID: PMC6004242
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.02.011
Two-Year Outcomes of Sacral Neuromodulation Versus OnabotulinumtoxinA for Refractory Urgency Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Trial
Abstract
Background: Urgency urinary incontinence (UUI) is a chronic condition for which sacral neuromodulation (SNM) (InterStim/Medtronic) and onabotulinumtoxinA (BTX) (BotoxA/Allergan) are utilized. These therapies have not been compared over extended time.
Objective: To compare UUI episodes (UUIE) over 24 mo following SNM or BTX.
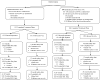
Design, setting, and participants: Multicenter, open-label, randomized, extension trial (February 2012-July 2016) at nine US medical centers involving 386 women with ≥6 UUIE over 3 d inadequately managed by medications. Participants were clinical responders to treatment: ≥50% reduction in UUIEs after SNM placement or 1 mo post BTX.
Intervention: SNM (n=194) versus 200 U BTX (n=192). SNM reprogrammings occurred throughout the 24 mo. After 6 mo, two additional BTX injections were allowed.
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Primary outcome: change in mean daily UUIE over 24 mo.
Secondary outcomes: no UUIE, ≥75% and ≥50% UUIE reduction; Overactive Bladder Questionnaire Short Form; Urinary Distress Inventory short form; Incontinence Impact Questionnaire; Patient Global Impression of Improvement; Overactive Bladder Satisfaction of Treatment Questionnaire; and adverse events (AEs). Primary analysis used a linear mixed model.
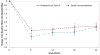
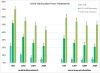
Results and limitations: Outcome data were available for 260/298 (87%) clinical responders. No difference in decreased mean UUIE was found over 24 mo (-3.88 vs -3.50 episodes/d,95% confidence interval [CI]=-0.14-0.89; p=0.15), with no differences in UUI resolution, ≥75% or ≥50% UUIE reduction. BTX group maintained higher satisfaction (mean difference=-9.14, 95% CI=-14.38--3.90; p<0.001), treatment endorsement (mean difference=-12.16, 95% CI=-17.7--6.63; p<0.001) through 24 mo. Other secondary measures did not differ. Recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) were higher after BTX (24% vs 10%; p<0.01), 6% required intermittent catheterization post second injection. SNM revision and removals occurred in 3% and 9% patients, respectively.
Conclusions: Both treatments offered sustainable UUI improvement, and higher BTX dosing had low clean intermittent catheterization rates, but with UTI risk. SNM revision/removal rates were low due to standardized lead placement with strict treatment response definitions.
Patient summary: We compared a large group of US women with severe urgency urinary incontinence (UUI) who received sacral neuromodulation (InterStim) or onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox A) therapy during a 2-yr period. We found that both therapies had similar success in reducing UUI symptoms, and adverse events were low. However, women in the BotoxA group had higher satisfaction and endorsement with their treatment, but with a higher chance of a urinary tract infection. We conclude that both therapies offer sustained reduction in daily incontinence over 2 yr.
Keywords: Botox; InterStim; OnbotulinumtoxinA; Sacral neuromodulation; Urgency urinary incontinence.
Copyright © 2018 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Sacral Neuromodulation and OnabotulinumtoxinA for Refractory Urge Urinary Incontinence Offer Similar Success During 2-Year Follow-up.Eur Urol. 2018 Jul;74(1):74-75. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.03.016. Epub 2018 Apr 8. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 29636255 No abstract available.
References
-
- Abrams P, Kelleher C, Kerr LA, Rogers RG. Overactive bladder significantly affects quality of life. Am J Manag Care. 2000;6:S580–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 HD041261/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD069013/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD041249/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD054215/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD054214/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD069006/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD069010/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD069013/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041267/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD054214/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD069006/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD069010/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD041267/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD054136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD054241/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041250/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD041261/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HD069031/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD069025/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

