Depth and durability of response to ibrutinib in CLL: 5-year follow-up of a phase 2 study
- PMID: 29483101
- PMCID: PMC5969380
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-12-820910
Depth and durability of response to ibrutinib in CLL: 5-year follow-up of a phase 2 study
Abstract
The safety and efficacy of ibrutinib (420 mg) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) were evaluated in a phase 2 study; 51 patients had TP53 aberration (TP53 cohort) and 35 were enrolled because of age 65 years or older (elderly cohort). Both cohorts included patients with treatment-naive (TN) and relapsed/refractory (RR) CLL. With the median follow-up of 4.8 years, 49 (57.0%) of 86 patients remain on study. Treatment was discontinued for progressive disease in 20 (23.3%) patients and for adverse events in 5 (5.8%). Atrial fibrillation occurred in 18 (20.9%) patients for a rate of 6.4 per 100 patient-years. No serious bleeding occurred. The overall response rate at 6 months, the primary study endpoint, was 95.8% for the TP53 cohort (95% confidence interval, 85.7%-99.5%) and 93.9% for the elderly cohort (95% confidence interval, 79.8%-99.3%). Depth of response improved with time: at best response, 14 (29.2%) of 48 patients in the TP53 cohort and 9 (27.3%) of 33 in the elderly cohort achieved a complete response. Median minimal residual disease (MRD) in peripheral blood was 3.8 × 10-2 at 4 years, with MRD-negative (<10-4) remissions in 5 (10.2%) patients. In the TP53 cohort, the estimated 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 74.4% in TN-CLL compared with 19.4% in RR-CLL (P = .0002), and overall survival (OS) was 85.3% vs 53.7%, respectively (P = .023). In the elderly cohort, the estimated 5-year PFS and OS in RR-CLL were 64.8% and 71.6%, respectively, and no event occurred in TN-CLL. Long-term administration of ibrutinib was well tolerated and provided durable disease control for most patients. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01500733.
© 2018 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.Z.H.F. is employed by Merck, owns stocks, and has received travel support from Merck. A.W. received research support from Pharmacyclics. N.S.S. received research support from Pharmacyclics. C.U.N. received consultancy fees and/or travel grants outside the current study from Janssen, AbbVie, Novartis, Gilead, and Roche. C.H.G. received consultancy fees from Janssen and Celgene and research support from Novo Nordisk. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
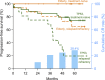


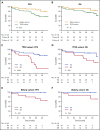
Comment in
-
Five years of ibrutinib in CLL.Blood. 2018 May 24;131(21):2280-2281. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-03-837864. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29794077 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fischer K, Bahlo J, Fink AM, et al. Long-term remissions after FCR chemoimmunotherapy in previously untreated patients with CLL: updated results of the CLL8 trial. Blood. 2016;127(2):208-215. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M, Fischer K, Fingerle-Rowson G, et al. ; German Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Study Group. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9747):1164-1174. - PubMed
-
- Stilgenbauer S, Schnaiter A, Paschka P, et al. Gene mutations and treatment outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results from the CLL8 trial. Blood. 2014;123(21):3247-3254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

