Genomic and Functional Fidelity of Small Cell Lung Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts
- PMID: 29483136
- PMCID: PMC6369413
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0935
Genomic and Functional Fidelity of Small Cell Lung Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts
Abstract
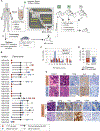
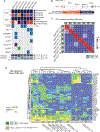
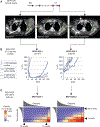
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patient-derived xenografts (PDX) can be generated from biopsies or circulating tumor cells (CTC), though scarcity of tissue and low efficiency of tumor growth have previously limited these approaches. Applying an established clinical-translational pipeline for tissue collection and an automated microfluidic platform for CTC enrichment, we generated 17 biopsy-derived PDXs and 17 CTC-derived PDXs in a 2-year timeframe, at 89% and 38% efficiency, respectively. Whole-exome sequencing showed that somatic alterations are stably maintained between patient tumors and PDXs. Early-passage PDXs maintain the genomic and transcriptional profiles of the founder PDX. In vivo treatment with etoposide and platinum (EP) in 30 PDX models demonstrated greater sensitivity in PDXs from EP-naïve patients, and resistance to EP corresponded to increased expression of a MYC gene signature. Finally, serial CTC-derived PDXs generated from an individual patient at multiple time points accurately recapitulated the evolving drug sensitivities of that patient's disease. Collectively, this work highlights the translational potential of this strategy.Significance: Effective translational research utilizing SCLC PDX models requires both efficient generation of models from patients and fidelity of those models in representing patient tumor characteristics. We present approaches for efficient generation of PDXs from both biopsies and CTCs, and demonstrate that these models capture the mutational landscape and functional features of the donor tumors. Cancer Discov; 8(5); 600-15. ©2018 AACR.This article is highlighted in the In This Issue feature, p. 517.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
B.J. Drapkin reports receiving commercial research support from Novartis. M. Mino-Kenudson is a consultant/advisory board member for H3 Biomedicine and Merrimack Pharmaceuticals. S. Lakis is a consultant/advisory board member for BioNTech Diagnostics. R.S. Heist is a consultant/advisory board member for Boehringer Ingelheim. R. Büttner is a consultant/advisory board member for AbbVie. L. V. Sequist is a consultant/advisory board member for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Genentech, Merrimack, Novartis, and Pfizer. A.N. Hata reports receiving commercial research grants from Amgen, Novartis, and Relay Therapeutics. S. Maheswaran has applied for patent protection for the CTC isolation technology. D.A. Haber has applied for patent protection for the CTC isolation technology. N. Dyson reports receiving commercial research support from Novartis. R.K. Thomas reports receiving a commercial research grant from Roche; has received honoraria from the speakers bureaus of AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Clovis, Daiichi-Sankyo, Lilly, Merck, MSD, Puma, and Roche; and is a consultant/advisory board member for Neo New Oncology GmbH. A.F. Farago reports receiving commercial research support from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Novartis, PharmaMar, Loxo Oncology, Ignyta, Merck, and Bristol-Myers Squibb; has received honoraria from the speakers bureau of Foundation Medicine; and is a consultant/advisory board member of AbbVie, PharmaMar, Loxo, Takeda, and Merrimack. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures


References
-
- Jalal SI, Lavin P, Lo G, Lebel F, Einhorn L. Carboplatin and etoposide with or without palifosfamide in untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: a multicenter, adaptive, randomized phase III study (MATISSE). J Clin Oncol 2017;35:2619–23. - PubMed
-
- Tiseo M, Boni L, Ambrosio F, Camerini A, Baldini E, Cinieri S, et al. Italian, multicenter, phase III, randomized study of cisplatin plus etoposide with or without bevacizumab as first-line treatment in extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: the GOIRC-AIFA FARM6P- MFJM Trial. J Clin Oncol 2017;35:1281–7. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Luft A, Szczesna A, Havel L, Kim SW, Akerley W, et al. Phase III randomized trial of ipilimumab plus etoposide and platinum versus placebo plus etoposide and platinum in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2016;34:3740–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

