Combined Inhibition of mTOR and CDK4/6 Is Required for Optimal Blockade of E2F Function and Long-term Growth Inhibition in Estrogen Receptor-positive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 29483206
- PMCID: PMC6485624
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0537
Combined Inhibition of mTOR and CDK4/6 Is Required for Optimal Blockade of E2F Function and Long-term Growth Inhibition in Estrogen Receptor-positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
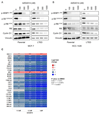
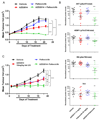
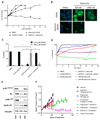
The cyclin dependent kinase (CDK)-retinoblastoma (RB)-E2F pathway plays a critical role in the control of cell cycle in estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer. Small-molecule inhibitors of CDK4/6 have shown promise in this tumor type in combination with hormonal therapies, reflecting the particular dependence of this subtype of cancer on cyclin D1 and E2F transcription factors. mTOR inhibitors have also shown potential in clinical trials in this disease setting. Recent data have suggested cooperation between the PI3K/mTOR pathway and CDK4/6 inhibition in preventing early adaptation and eliciting growth arrest, but the mechanisms of the interplay between these pathways have not been fully elucidated. Here we show that profound and durable inhibition of ER+ breast cancer growth is likely to require multiple hits on E2F-mediated transcription. We demonstrate that inhibition of mTORC1/2 does not affect ER function directly, but does cause a decrease in cyclin D1 protein, RB phosphorylation, and E2F-mediated transcription. Combination of an mTORC1/2 inhibitor with a CDK4/6 inhibitor results in more profound effects on E2F-dependent transcription, which translates into more durable growth arrest and a delay in the onset of resistance. Combined inhibition of mTORC1/2, CDK4/6, and ER delivers even more profound and durable regressions in breast cancer cell lines and xenografts. Furthermore, we show that CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant cell lines reactivate the CDK-RB-E2F pathway, but remain sensitive to mTORC1/2 inhibition, suggesting that mTORC1/2 inhibitors may represent an option for patients that have relapsed on CDK4/6 therapy. Mol Cancer Ther; 17(5); 908-20. ©2018 AACR.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest
Figures



References
-
- Turner NC, Neven P, Loibl S, Andre F. Advances in the treatment of advanced oestrogen-receptor positive breast cancer. Lancet. 2017;389(10087):2403–2414. - PubMed
-
- Jerusalem G, Bachelot T, Barrios C, Neven P, Di Leo A, Janni W, et al. A new era of improving progression-free survival with dual blockade in postmenopausal HR(+), HER2(-) advanced breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015;41:94–104. - PubMed
-
- Chumsri S, Sabnis G, Tkaczuk K, Brodie A. mTOR inhibitors: changing landscape of endocrine-resistant breast cancer. Future Oncol. 2014;10:443–456. - PubMed
-
- Palanisamy RP. Palbociclib: A new hope in the treatment of breast cancer. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016;12(4):1220–1223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

