The effectiveness, reproducibility, and durability of tailored mobile coaching on diabetes management in policyholders: A randomized, controlled, open-label study
- PMID: 29483559
- PMCID: PMC5827660
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-22034-0
The effectiveness, reproducibility, and durability of tailored mobile coaching on diabetes management in policyholders: A randomized, controlled, open-label study
Abstract
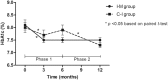
This randomized, controlled, open-label study conducted in Kangbuk Samsung Hospital evaluated the effectiveness, reproducibility, and durability of tailored mobile coaching (TMC) on diabetes management. The participants included 148 Korean adult policyholders with type 2 diabetes divided into the Intervention-Maintenance (I-M) group (n = 74) and Control-Intervention (C-I) group (n = 74). Intervention was the addition of TMC to typical diabetes care. In the 6-month phase 1, the I-M group received TMC, and the C-I group received their usual diabetes care. During the second 6-month phase 2, the C-I group received TMC, and the I-M group received only regular information messages. After the 6-month phase 1, a significant decrease (0.6%) in HbA1c levels compared with baseline values was observed in only the I-M group (from 8.1 ± 1.4% to 7.5 ± 1.1%, P < 0.001 based on a paired t-test). At the end of phase 2, HbA1c levels in the C-I group decreased by 0.6% compared with the value at 6 months (from 7.9 ± 1.5 to 7.3 ± 1.0, P < 0.001 based on a paired t-test). In the I-M group, no changes were observed. Both groups showed significant improvements in frequency of blood-glucose testing and exercise. In conclusion, addition of TMC to conventional treatment for diabetes improved glycemic control, and this effect was maintained without individualized message feedback.
Conflict of interest statement
J.W.P. and D.A.C. were employed by Huraypositive Inc.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources