Olfactory stimulation modulates the blood glucose level in rats
- PMID: 29483818
- PMCID: PMC5820856
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.21528
Olfactory stimulation modulates the blood glucose level in rats
Abstract
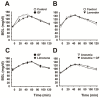
In both humans and animals, chemosensory stimuli, including odors and tastes, induce a variety of physiologic and mental responses related to energy homeostasis, such as glucose kinetics. The present study examined the importance of olfactory function in glucose kinetics following ingestion behavior in a simplified experimental scenario. We applied a conventional glucose tolerance test to rats with and without olfactory function and analyzed subsequent blood glucose (BG) curves in detail. The loss of olfactory input due to experimental damage to the olfactory mucosa induced a marked decrease in the area under the BG curve. Exposure to grapefruit odor and its main component, limonene, both of which activate the sympathetic nerves, before glucose loading also greatly depressed the BG curve. Pre-loading exposure to lavender odor, a parasympathetic activator, stabilized the BG level. These results suggest that olfactory function is important for proper glucose kinetics after glucose intake and that certain fragrances could be utilized as tools for controlling BG levels.
Keywords: blood glucose; glucose tolerance test; odor; the area under the curve of blood glucose.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Olfactory stimulatory with grapefruit and lavender oils change autonomic nerve activity and physiological function.Auton Neurosci. 2014 Oct;185:29-35. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2014.06.005. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Auton Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25002406 Review.
-
Spatial Mapping in the Rat Olfactory Bulb by Odor and Direct Electrical Stimulation.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Sep;155(3):526-32. doi: 10.1177/0194599816646358. Epub 2016 May 10. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016. PMID: 27165674
-
Olfactory stimulation with scent of essential oil of grapefruit affects autonomic neurotransmission and blood pressure.Brain Res. 2005 Oct 5;1058(1-2):44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.07.048. Epub 2005 Oct 5. Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 16168968
-
Cat odor, but not trimethylthiazoline (fox odor), activates accessory olfactory and defense-related brain regions in rats.Neuroscience. 2008 Feb 19;151(4):937-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.11.039. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18201833
-
Understanding smell--the olfactory stimulus problem.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013 Sep;37(8):1667-79. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.06.009. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013. PMID: 23806440 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhalation of Patchouli (Pogostemon Cablin Benth.) Essential Oil Improved Metabolic Parameters in Obesity-Induced Sprague Dawley Rats.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 13;12(7):2077. doi: 10.3390/nu12072077. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32668680 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory Stimulation by Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.) Essential Oil Improves Lipid Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders in High Fat-Induced Obese Rats.Nutrients. 2022 Feb 10;14(4):741. doi: 10.3390/nu14040741. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35215391 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory Dysfunction: A Complication of Diabetes or a Factor That Complicates Glucose Metabolism? A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2021 Nov 29;10(23):5637. doi: 10.3390/jcm10235637. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34884338 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Niijima A. Nervous regulation of metabolism. Prog Neurobiol. 1989;33:135–47. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd GM. Smell images and the flavour system in the human brain. Nature. 2006;444:316–21. - PubMed
-
- Abdallah L, Chabert M, Louis-Sylvestre J. Cephalic phase responses to sweet taste. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997;65:737–43. - PubMed
-
- Niijima A. Effects of taste stimulation on the efferent activity of the autonomic nerves in the rat. Brain Res Bull. 1991;26:165–7. - PubMed
-
- Inui-Yamamoto C, Furudono Y, Yamamoto T. Hedonics of taste influence the gastric emptying in rats. Physiol Behav. 2009;96:717–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

