Cutaneous manifestations of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- PMID: 29484103
- PMCID: PMC5821163
- DOI: 10.1080/19381980.2017.1395537
Cutaneous manifestations of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Abstract
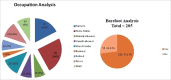
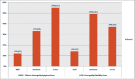
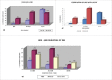
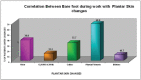
There is a rise in number of people diagnosed with Diabetes Mellitus. The incidence is rising in modern Indian society because of Industrial development and drastically changing lifestyles. Diabetic neuropathies are microvascular disorders that are usually associated with the duration of Diabetes. Among the various forms, the most common is Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. The disease if neglected leads to chronic ulcer formation leading to amputations frequently. Hence the aim of this study is to document the early cutaneous changes and create an early awareness in the importance of controlling Diabetes. The study consisted of 205 patients with Type 2 DM. Participant's neuropathy status was determined based on Neuropathy Disability Score and Diabetic Neuropathy Symptom Score. Among the Skin changes documented, the common changes seen were: Peripheral hair loss in 185 (90.2%), Xerosis in 168 (82%), Anhydrosis in 162 (79%), Plantar Fissures in 136 (66.3%), Plantar Ulcer in 80 (39%), common nail changes documented were Onychomycosis in 165 (80.5%) and Onychauxis in 53 (25.8%) patients in relation to the occupation and duration of Diabetes mellitus. In conclusion, it is important to control glycemic levels in the all stages of Diabetes and institute foot care measures to prevent the complications of neuropathy.
Keywords: Cutaneous Manifestations; Diabetes; Diabetic Neuropathy Symptom Score; Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy; Neuropathy Disability Score.
Figures


References
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 2001;13;414(6865):782–7. - PubMed
-
- Dyck PJ. Detection, characterization, and staging of polyneuropathy: assessed in diabetics. Muscle Nerve 1988;11:21–32. - PubMed
-
- Young MJ, Boulton AJ, MacLeod AF, Williams DR, Sonksen PH. A multicentre study of the prevalence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in the United Kingdom hospital clinic population. Diabetologia 1993;36(2):150–4. - PubMed
-
- Dyck PJ, Boes CJ, Mulder D, Millikan C, Windebank AJ, Dyck PJ, Espinosa R. History of standard scoring, notation, and summation of neuromuscular signs. Acurrent survey and recommendation. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2005;10:158–173. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
