Dynamic MRI and isotope renogram in the functional evaluation of pelviureteric junction obstruction: A comparative study
- PMID: 29484227
- PMCID: PMC5821282
- DOI: 10.5152/tud.2018.08365
Dynamic MRI and isotope renogram in the functional evaluation of pelviureteric junction obstruction: A comparative study
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare the diagnostic accuracy of dynamic contrast- enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) and isotope renogram in the functional evaluation of pelviureteric junction obstruction (PUJO).
Material and methods: Forty-two patients included in the study were investigated with isotope renogram and subsequently, subjected to dMRI. Time-activity curves were generated for both isotope renogram and dMRI. Out of the 42 cases, 9 cases were conservatively managed. Thirty-three cases were taken up for surgical intervention.
Results: Of 33 patients taken up for surgical intervention, 12 underwent laparoscopic nephrectomy and 21 of them pyeloplasty. The mean glomerular filtration rates (GFRs) as measured by isotope renogram and dMRI were 22.5+4.2 mL/min and 23.8+3.1 mL/min respectively. The calculation of GFR by isotope renogram, showed good correlation with that of dMRI with correlation coefficient of 0.93. The dMRI was able to reveal the functional status of the renal unit accurately. dMRI did not yield false positive results with 20 of 21 patients scheduled for pyeloplasty and 11 of 12 patients scheduled for nephrectomy. Isotope renogram had a false positive result in 3 cases compared with surgical diagnosis.
Conclusion: Analysis of renal function using dMRI yielded results comparable to those of renal scintigraphy, with superior spatial and contrast resolution. It was also better in prompting management decisions with respect to the obstructed systems. dMRI can be used as a "one stop imaging examination" that can replace different imaging methods used for morphological, etiological and functional evaluation of PUJO.
Keywords: MRI; nuclear medicine; obstruction; pelviureteric junction.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
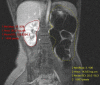
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pelviureteric Junction Obstruction Due to Vascular Anomalies in Children - Simple Surgical Options.J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2022 May-Jun;27(3):297-303. doi: 10.4103/jiaps.JIAPS_28_21. Epub 2022 May 12. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2022. PMID: 35733588 Free PMC article.
-
Calyx to Parenchymal Ratio (CPR): An unexplored tool and its utility in the follow-up of pyeloplasty.J Pediatr Urol. 2021 Apr;17(2):234.e1-234.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2021.01.004. Epub 2021 Jan 11. J Pediatr Urol. 2021. PMID: 33582018
-
Can we improve the usefulness of the diuretic renogram in the diagnosis of ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) in children? Introduction of mercaptoacetyltriglycine-suspected obstruction scoring system (MAG-SOS).J Pediatr Urol. 2023 Jun;19(3):311.e1-311.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2023.02.022. Epub 2023 Mar 2. J Pediatr Urol. 2023. PMID: 36922332
-
Antenatal detection of pelviureteric junction stenosis: main controversies.Semin Nucl Med. 2011 Jan;41(1):11-9. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2010.07.008. Semin Nucl Med. 2011. PMID: 21111856 Review.
-
Forming a stone in pelviureteric junction obstruction: Cause or effect?Int Braz J Urol. 2017 Jan-Feb;43(1):13-19. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0515. Int Braz J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28124521 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report; Concomitant Left Nutcracker Syndrome and Right Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction.Res Rep Urol. 2024 Jun 10;16:131-135. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S446710. eCollection 2024. Res Rep Urol. 2024. PMID: 38883265 Free PMC article.
-
A novel method for estimating the urine drainage time from the renal collecting system.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 Jun;46(6):2647-2655. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02880-1. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021. PMID: 33386909
-
Improving Automatic Renal Segmentation in Clinically Normal and Abnormal Paediatric DCE-MRI via Contrast Maximisation and Convolutional Networks for Computing Markers of Kidney Function.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Nov 28;21(23):7942. doi: 10.3390/s21237942. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34883946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neste MG, du Cret RP, Finlay DE, Sane S, Gonzalez R, Boudreau RJ, et al. Postoperative diuresis renography and ultrasound in patients undergoing pyeloplasty. Predictors of surgical outcome. Clin Nucl Med. 1993;18:872–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003072-199310000-00010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- O’Reilly P, Aurell M, Britton K, Kletter K, Rosenthal L, Testa T. Consensus on diuresis renography for investigating the dilated upper urinary tract. Radionuclides in Nephrourology Group. Consensus Committee on Diuresis Renography. J Nucl Med. 1996;37:1872–6. - PubMed
-
- Lawler LP, Jarret TW, Corl FM, Fishman EK. Adult ureteropelvic junction obstruction: insights with three-dimensional multi-detector row CT. Radiographics. 2005;25:121–34. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.251045510. - DOI - PubMed
-
- MacNeily AE, Maizels M, Conway JJ. Does early Pyeloplasty really avert loss of Renal function? A Retrospective view. J Urol. 1993;150:769–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)35610-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gonzales R, Schimke CM. Pelvic-Ureteric Junction Obstruction in Infants and children. Paediat Clin North AM. 2001;48:1505–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3955(05)70388-6. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
