Inhibition of cell migration by focal adhesion kinase: Time-dependent difference in integrin-induced signaling between endothelial and hepatoblastoma cells
- PMID: 29484384
- PMCID: PMC5846670
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3512
Inhibition of cell migration by focal adhesion kinase: Time-dependent difference in integrin-induced signaling between endothelial and hepatoblastoma cells
Abstract
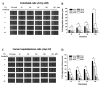
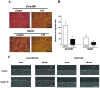
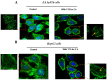
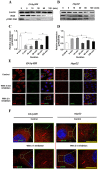
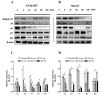
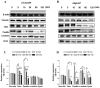
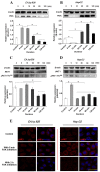
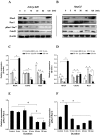
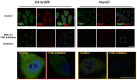
angiogenesis plays an important role in the development and progression of tumors, and it involves a series of signaling pathways contributing to the migration of endothelial cells for vascularization and to the invasion of cancer cells for secondary tumor formation. Among these pathways, the focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling cascade has been implicated in a variety of human cancers in connection with cell adhesion and migration events leading to tumor angiogenesis, metastasis and invasion. Therefore, the inhibition of FAK in endothelial and/or cancer cells is a potential target for anti‑angiogenic therapy. In the present study, a small‑molecule FAK inhibitor, 1,2,4,5-benzenetetramine tetrahydrochloride (Y15), was used to study the effects of FAK inhibition on the adhesion and migration behaviors of vascular endothelial cells (VECs) and human hepatoblastoma cells. Furthermore, the time-dependent differences in proteins associated with the integrin-mediated FAK/Rho GTPases signaling pathway within 2 h were examined. The results indicated that the inhibition of FAK significantly decreased the migration ability of VECs and human hepatoblastoma cells in a dose-dependent manner. Inhibition of FAK promoted cell detachment by decreasing the expression of focal adhesion components, and blocked cell motility by reducing the level of Rho GTPases. However, the expression of crucial proteins involved in integrin-induced signaling in two cell lines exhibited a time-dependent difference with increased duration of FAK inhibitor treatment, suggesting different mechanisms of FAK-mediated cell migration behavior. These results suggest that the mechanism underlying FAK-mediated adhesion and migration behavior differs among various cells, which is expected to provide evidence for future FAK therapy targeted against tumor angiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

