The rs626283 Variant in the MBOAT7 Gene is Associated with Insulin Resistance and Fatty Liver in Caucasian Obese Youth
- PMID: 29485130
- PMCID: PMC12136689
- DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2018.1
The rs626283 Variant in the MBOAT7 Gene is Associated with Insulin Resistance and Fatty Liver in Caucasian Obese Youth
Abstract
Objectives: Non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a leading cause of liver damage in childhood, its occurrence is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Recently, the rs626283 polymorphism in the MBOAT7 gene has been found to be associated with alcoholic liver disease and NAFLD in adults.
Methods: In a multiethnic cohort of obese children and adolescents we genotyped the rs626283 polymorphism in the MBOAT7 gene, evaluated insulin sensitivity by an oral glucose tolerance test, and measured the intra-hepatic fat content (HFF%) by magnetic resonance imaging.
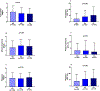
Results: In Caucasian youth, the minor allele (C) was associated with HFF% in (P=0.003), fasting insulin (P=0.03), area under the curve of glucose (P=0.03), and lower degree of whole-body insulin sensitivity (P=0.01) independent of age, gender, and body mass index z-score. A partial correlation showed that the association between the rs626283 variant and insulin resistance was driven by the presence of hepatic steatosis (P=0.009). However, there was no association between the rs626283 and hepatic steatosis among Hispanic and African American children and youth. The association between the rs626283 in the MBOAT7 gene among Caucasians was independent of the PNPLA3 rs738409, GCKR 1260326, and TM6SF2 rs58542926 (P=0.01). The four polymorphisms combined explained~19% of the HFF% in Caucasian obese children and adolescents.
Conclusions: The rs626283 variant in the MBOAT7 gene is associated with NAFLD and may affect glucose metabolism by modulating intra-hepatic fat content in Caucasian obese children and adolescents.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest/study support
Figures
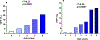
References
-
- D’Adamo E, Santoro N, Caprio S. Metabolic syndrome in pediatrics: old concepts revised, new concepts discussed. Pediatr Clin North Am 2011;58:1241–55, xi. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

