Testing the evidence integration triangle for implementation of interventions to manage behavioral and psychological symptoms associated with dementia: Protocol for a pragmatic trial
- PMID: 29485197
- PMCID: PMC6400658
- DOI: 10.1002/nur.21866
Testing the evidence integration triangle for implementation of interventions to manage behavioral and psychological symptoms associated with dementia: Protocol for a pragmatic trial
Abstract
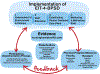
Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) include aggression, agitation, resistiveness to care, depression, anxiety, apathy, and hallucinations. BPSD are common in nursing home residents and can be ameliorated using person-centered approaches. Despite regulatory requirements, less than 2% of nursing homes consistently implement person-centered behavioral approaches. In a National Institute of Nursing Research-funded research protocol, we are implementing a pragmatic cluster randomized clinical trial designed to enable staff in nursing homes to reduce BPSD using behavioral approaches while optimizing function, preventing adverse events, and improving quality of life of residents. The implementation is based on use of the Evidence Integration Triangle (EIT), a parsimonious, community-engaged participatory framework that is well suited to the complexity and variability in the nursing home environment. A total of 50 nursing home communities will be randomized to EIT-4-BPSD or education only. Primary Aim 1 is to determine if communities exposed to EIT-4-BPSD demonstrate evidence of implementation evaluated by the Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, and Maintenance (RE-AIM) criteria. Primary Aim 2 is to evaluate the feasibility, utility, and cost of the EIT approach in EIT-4-BPSD communities.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; behavioral and psychological symptoms; nursing home; pragmatic trial.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Process evaluation of an implementation study in dementia care (EIT-4-BPSD): stakeholder perspectives.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Sep 23;21(1):1006. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-07001-2. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34551782 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Implementation of the Evidence Integration Triangle for behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (EIT-4-BPSD) in care communities.Nurs Outlook. 2021 Nov-Dec;69(6):1058-1071. doi: 10.1016/j.outlook.2021.06.004. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Nurs Outlook. 2021. PMID: 34332762 Free PMC article.
-
Pilot Testing of the EIT-4-BPSD Intervention.Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2016 Nov;31(7):570-579. doi: 10.1177/1533317516662337. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2016. PMID: 27609932 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of non-pharmacological interventions for BPSD in nursing home residents with dementia: from a perspective of ergonomics.Int Psychogeriatr. 2019 Aug;31(8):1137-1149. doi: 10.1017/S1041610218001679. Int Psychogeriatr. 2019. PMID: 30334500
-
[Methodological and regulatory features of clinical trials for behavioral and psychological symptoms in the course of dementia].Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2003;39(2):267-74. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2003. PMID: 14587227 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Factor Analysis of the Short-Form Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory and the Measurement Invariance by Gender.J Nurs Meas. 2021 Dec 1;29(3):523-540. doi: 10.1891/JNM-D-20-00031. Epub 2021 Sep 13. J Nurs Meas. 2021. PMID: 34518408 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
12-month trajectory and predictors of affect balance in nursing home residents living with dementia.Aging Ment Health. 2022 Aug;26(8):1686-1692. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2021.1947964. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Aging Ment Health. 2022. PMID: 34253099 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reliability and Validity of the Knowledge of Person-Centered Behavioral Approaches for BPSD Test.J Nurs Meas. 2020 Dec 1;28(3):472-488. doi: 10.1891/JNM-D-19-00016. Epub 2020 Oct 16. J Nurs Meas. 2020. PMID: 33067367 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing integrated care evaluation in shifting contexts: blending implementation research with case study design in project SUSTAIN.BMC Health Serv Res. 2020 Oct 23;20(1):971. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05775-5. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020. PMID: 33097038 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and Validity Testing of the Assessment of the Environment for Person-Centered Management of BPSD and Assessment of Policies for Person-Centered Management of BPSD Measures.J Aging Environ. 2020;34(3):310-331. Epub 2020 Jan 28. J Aging Environ. 2020. PMID: 34378006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexopoulos G, Abrams R, Young R, & Shamoian C (1988a). Cornell scale for depression in dementia. Biology and Psychiatry, 23, 271–284. - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulos GS, Abrams RC, Young RC, & Shamoian CA (1988b). Use of the Cornell Scale in non-demented patients. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 36, 230–236. - PubMed
-
- American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN) (2008). Cultural competency in baccalaureate nursing education, Retrieved from http://www.aacnnursing.org/Education-Resources/Tool-Kits/Cultural-Compet...
-
- Bandura A (1986). Social Foundations of Thought and Action Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
-
- Bandura A (1995). Self-efficacy in Changing Societies New York: Cambridge University Press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
