Gradient Material Strategies for Hydrogel Optimization in Tissue Engineering Applications
- PMID: 29485612
- PMCID: PMC5876527
- DOI: 10.3390/ht7010001
Gradient Material Strategies for Hydrogel Optimization in Tissue Engineering Applications
Abstract
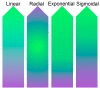
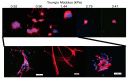
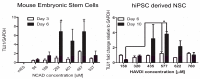
Although a number of combinatorial/high-throughput approaches have been developed for biomaterial hydrogel optimization, a gradient sample approach is particularly well suited to identify hydrogel property thresholds that alter cellular behavior in response to interacting with the hydrogel due to reduced variation in material preparation and the ability to screen biological response over a range instead of discrete samples each containing only one condition. This review highlights recent work on cell-hydrogel interactions using a gradient material sample approach. Fabrication strategies for composition, material and mechanical property, and bioactive signaling gradient hydrogels that can be used to examine cell-hydrogel interactions will be discussed. The effects of gradients in hydrogel samples on cellular adhesion, migration, proliferation, and differentiation will then be examined, providing an assessment of the current state of the field and the potential of wider use of the gradient sample approach to accelerate our understanding of matrices on cellular behavior.
Keywords: cell–material interface; combinatorial method; gradient.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combinatorial Method/High Throughput Strategies for Hydrogel Optimization in Tissue Engineering Applications.Gels. 2016 Jun 8;2(2):18. doi: 10.3390/gels2020018. Gels. 2016. PMID: 30674150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanical stabilization of proteolytically degradable polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate hydrogels through peptide interaction.Acta Biomater. 2018 Apr 15;71:271-278. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29526829
-
Gradient Hydrogels.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2021;178:227-251. doi: 10.1007/10_2020_155. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33219386
-
Concentration dependent survival and neural differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells cultured on polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate hydrogels possessing a continuous concentration gradient of n-cadherin derived peptide His-Ala-Val-Asp-Lle.Acta Biomater. 2017 Jul 1;56:153-160. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.063. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27915022
-
Enzyme-Laden Bioactive Hydrogel for Biocatalytic Monitoring and Regulation.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Mar 2;54(5):1274-1287. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00832. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33570397 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Laminin Derived Peptides IKVAV and LRE Tethered to Hyaluronic Acid on hiPSC Derived Neural Stem Cell Morphology, Attachment and Neurite Extension.J Funct Biomater. 2020 Mar 6;11(1):15. doi: 10.3390/jfb11010015. J Funct Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32155839 Free PMC article.
-
Gradient scaffolds in bone-soft tissue interface engineering: Structural characteristics, fabrication techniques, and emerging trends.J Orthop Translat. 2025 Jan 28;50:333-353. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.10.015. eCollection 2025 Jan. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 39944791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on the Design of Hydrogels With Different Stiffness and Their Effects on Tissue Repair.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jan 25;10:817391. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.817391. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35145958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in hydrogel design for articular cartilage regeneration: A comprehensive review.Bioact Mater. 2024 Sep 14;43:1-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.09.005. eCollection 2025 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 39318636 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

