Shortening the decade-long gap between adult and paediatric drug formulations: a new framework based on the HIV experience in low- and middle-income countries
- PMID: 29485727
- PMCID: PMC5978668
- DOI: 10.1002/jia2.25049
Shortening the decade-long gap between adult and paediatric drug formulations: a new framework based on the HIV experience in low- and middle-income countries
Abstract
Introduction: Despite the coordinated efforts by several stakeholders to speed up access to HIV treatment for children, development of optimal paediatric formulations still lags 8 to 10 years behind that of adults, due mainly to lack of market incentives and technical complexities in manufacturing. The small and fragmented paediatric market also hinders launch and uptake of new formulations. Moreover, the problems affecting HIV similarly affect other disease areas where development and introduction of optimal paediatric formulations is even slower. Therefore, accelerating processes for developing and commercializing optimal paediatric drug formulations for HIV and other disease areas is urgently needed.
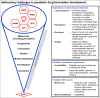
Discussion: The Global Accelerator for Paediatric Formulations (GAP-f) is an innovative collaborative model that will accelerate availability of optimized treatment options for infectious diseases, such as HIV, tuberculosis and viral hepatitis, affecting children in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). It builds on the HIV experience and existing efforts in paediatric drug development, formalizing collaboration between normative bodies, research networks, regulatory agencies, industry, supply and procurement organizations and funding bodies. Upstream, the GAP-f will coordinate technical support to companies to design and study optimal paediatric formulations, harmonize efforts with regulators and incentivize manufacturers to conduct formulation development. Downstream, the GAP-f will reinforce coordinated procurement and communication with suppliers. The GAP-f will be implemented in a three-stage process: (1) development of a strategic framework and promotion of key regulatory efficiencies; (2) testing of feasibility and results, building on the work of existing platforms such as the Paediatric HIV Treatment Initiative (PHTI) including innovative approaches to incentivize generic development and (3) launch as a fully functioning structure.
Conclusions: GAP-f is a key partnership example enhancing North-South and international cooperation on and access to science and technology and capacity building, responding to Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 17.6 (technology) and 17.9. (capacity-building). By promoting access to the most needed paediatric formulations for HIV and high-burden infectious diseases in low-and middle-income countries, GAP-f will support achievement of SDG 3.2 (infant mortality), 3.3 (end of AIDS and combat other communicable diseases) and 3.8 (access to essential medicines), and be an essential component of meeting the global Start Free, Stay Free, AIDS Free super-fast-track targets.
Keywords: Global Accelerator for Paediatric Formulations; HIV; drug development; drug formulations; paediatric drugs; regulatory approval; tuberculosis; viral hepatitis.
© 2018 World Health Organization; licensee IAS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Catalysing the development and introduction of paediatric drug formulations for children living with HIV: a new global collaborative framework for action.Lancet HIV. 2018 May;5(5):e259-e264. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(18)30005-5. Epub 2018 May 1. Lancet HIV. 2018. PMID: 29739700
-
Tuberculosis.In: Holmes KK, Bertozzi S, Bloom BR, Jha P, editors. Major Infectious Diseases. 3rd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2017 Nov 3. Chapter 11. In: Holmes KK, Bertozzi S, Bloom BR, Jha P, editors. Major Infectious Diseases. 3rd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2017 Nov 3. Chapter 11. PMID: 30212088 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Accelerating access to paediatric medicines: lessons learned from the Global Accelerator for Paediatric Formulations, a WHO-hosted network.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2025 May;9(5):337-348. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(25)00040-9. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2025. PMID: 40246360 Review.
-
Voluntary licensing of long-acting HIV prevention and treatment regimens: using a proven collaboration- and competition-based mechanism to rapidly expand at-scale, sustainable, quality-assured and affordable supplies in LMICs.J Int AIDS Soc. 2023 Jul;26 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):e26092. doi: 10.1002/jia2.26092. J Int AIDS Soc. 2023. PMID: 37439078 Free PMC article.
-
A lifeline to treatment: the role of Indian generic manufacturers in supplying antiretroviral medicines to developing countries.J Int AIDS Soc. 2010 Sep 14;13:35. doi: 10.1186/1758-2652-13-35. J Int AIDS Soc. 2010. PMID: 20840741 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Treating HIV-associated tuberculosis in children without compromise.Lancet HIV. 2025 Apr;12(4):e242-e244. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(24)00346-1. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Lancet HIV. 2025. PMID: 40023168 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Maximising the global health impact of future HIV cure-related interventions through advance planning.J Virus Erad. 2018 Jul 1;4(3):182-185. doi: 10.1016/S2055-6640(20)30266-1. J Virus Erad. 2018. PMID: 30050682 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Paediatric Regulation funding on the development of off-patent medicines in children.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 30;11:1473862. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1473862. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39949386 Free PMC article.
-
STACKing the odds for adolescent survival: health service factors associated with full retention in care and adherence amongst adolescents living with HIV in South Africa.J Int AIDS Soc. 2018 Sep;21(9):e25176. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25176. J Int AIDS Soc. 2018. PMID: 30240121 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pharmacologic Treatments for Children: Research Priorities and Approach to Pediatric Studies.Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Mar 15;72(6):1067-1073. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa885. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 32594142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS . UNAIDS Data 2017 [Internet]. Available from: http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/20170720_Data_book...
-
- Fast-Track: ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 [Internet]. Available from: http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/JC2686_WAD2014repo...
-
- Burger DM, Van Russum AM. Improved labelling of antiretrovirals for paediatric use. Lancet. 2016;3(12):e550–1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

